6 Pillars of aws
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/apn/the-6-pillars-of-the-aws-well-architected-framework/
1. Operational Excellence
The Operational Excellence pillar includes the ability to support development and run workloads effectively, gain insight into their operation, and continuously improve supporting processes and procedures to delivery business value
- Perform operations as code
- Make frequent, small, reversible changes
- Refine operations procedures frequently
- Anticipate failure
- Learn from all operational failures
2. Security
here are seven design principles for security in the cloud:
- Implement a strong identity foundation
- Enable traceability
- Apply security at all layers
- Automate security best practices
- Protect data in transit and at rest
- Keep people away from data
- Prepare for security events
3. Reliability
The Reliability pillar encompasses the ability of a workload to perform its intended function correctly and consistently when it’s expected to. This includes the ability to operate and test the workload through its total lifecycle.
- Automatically recover from failure
- Test recovery procedures
- Scale horizontally to increase aggregate workload availability
- Stop guessing capacity
- Manage change in automation
4. Performance Efficiency
- Democratize advanced technologies
- Go global in minutes
- Use serverless architectures
- Experiment more often
- Consider mechanical sympathy
5. Cost Optimization
- Implement cloud financial management
- Adopt a consumption model
- Measure overall efficiency
- Stop spending money on undifferentiated heavy lifting
- Analyze and attribute expenditure
6. Sustainability
The discipline of sustainability addresses the long-term environmental, economic, and societal impact of your business activities.
- Understand your impact
- Establish sustainability goals
- Maximize utilization
- Anticipate and adopt new, more efficient hardware and software offerings
- Use managed services
- Reduce the downstream impact of your cloud workloads
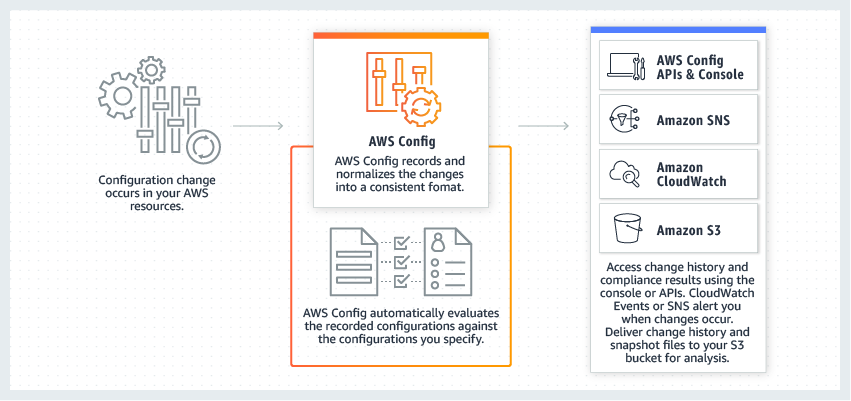
Aws config
AWS Config is a service that enables you to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of your AWS resources. Config continuously monitors and records your AWS resource configurations and allows you to automate the evaluation of recorded configurations against desired configurations.
AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail is a service that enables governance, compliance, operational auditing, and risk auditing of your AWS account. With CloudTrail, you can log, continuously monitor, and retain account activity related to actions across your AWS infrastructure. CloudTrail provides event history of your AWS account activity, including actions taken through the AWS Management Console, AWS SDKs, command-line tools, and other AWS services.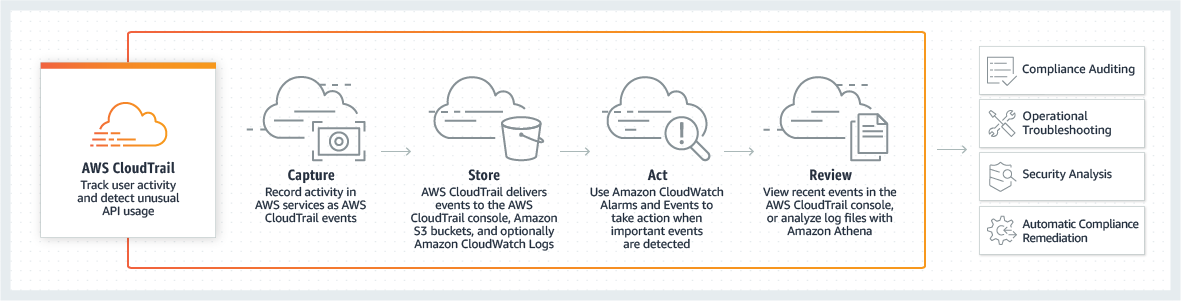
Amazon CloudWatch
Amazon CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service built for DevOps engineers, developers, site reliability engineers (SREs), and IT managers. CloudWatch provides data and actionable insights to monitor applications, respond to system-wide performance changes, optimize resource utilization, and get a unified view of operational health.
AWS Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor is an online tool that provides you real-time guidance to help you provision your resources following AWS best practices on cost optimization, security, fault tolerance, service limits, and performance improvement.
Amazon Inspector - Amazon Inspector is an automated security assessment service that helps improve the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS. Amazon Inspector automatically assesses applications for exposure, vulnerabilities, and deviations from best practices.
Amazon GuardDuty - Amazon GuardDuty is a threat detection service that monitors malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect your AWS account. GuardDuty analyzes billions of events across your AWS accounts from AWS CloudTrail (AWS user and API activity in your accounts), Amazon VPC Flow Logs (network traffic data), and DNS Logs (name query patterns). This service is for AWS account level access, not for instance-level management like an EC2. GuardDuty cannot be used to check OS vulnerabilities.
On-demand EC2 pricing is seconds based. Per-Second Billing for EC2 and EBS
ec2 pricings url RESERVED VS SAVINGS
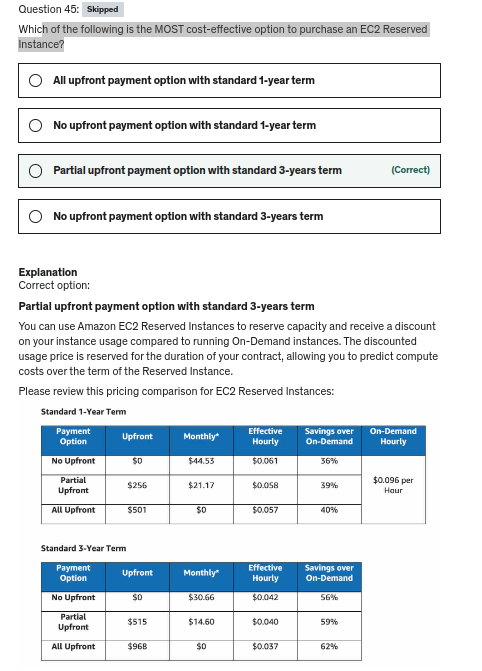
Amazon offers two pricing models for EC2 instances: EC2 Reserved Instances and Savings Plans. EC2 Reserved Instances provide you with a significant discount (up to 72%) compared to On-Demand Instance pricing, and can be purchased for a 1-year or 3-year term. Customers have the flexibility to change the Availability Zone, the instance size, and networking type of their Standard Reserved Instances. Purchase Convertible Reserved Instances if you need additional flexibility, such as the ability to use different instance families, operating systems, or tenancies over the Reserved Instance term. Convertible Reserved Instances provide you with a significant discount (up to 66%) compared to On-Demand Instances and can be purchased for a 1-year or 3-year term1.
Savings Plans is another flexible pricing model that provides savings of up to 72% on your AWS compute usage. This pricing model offers lower prices on Amazon EC2 instances usage, regardless of instance family, size, OS, tenancy or AWS Region, and also applies to AWS Fargate and AWS Lambda usage. Savings Plans offer significant savings over On-Demand Instances, just like EC2 Reserved Instances, in exchange for a commitment to use a specific amount of compute power (measured in $/hour) for a one or three-year period. You can sign up for Savings Plans for a one- or three-year term and easily manage your plans by taking advantage of recommendations, performance reporting and budget alerts in the AWS Cost Explorer2
Instance Store
An instance store provides temporary block-level storage for your instance. This storage is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer. This is a good option when you need storage with very low latency, but you don’t need the data to persist when the instance terminates or you can take advantage of fault-tolerant architectures. For this use-case, the computation application itself has a fault tolerant architecture, so it can automatically handle any failures of Instance Store volumes.
As the Instance Store volumes are included as part of the instance’s usage cost, therefore this is the correct option.
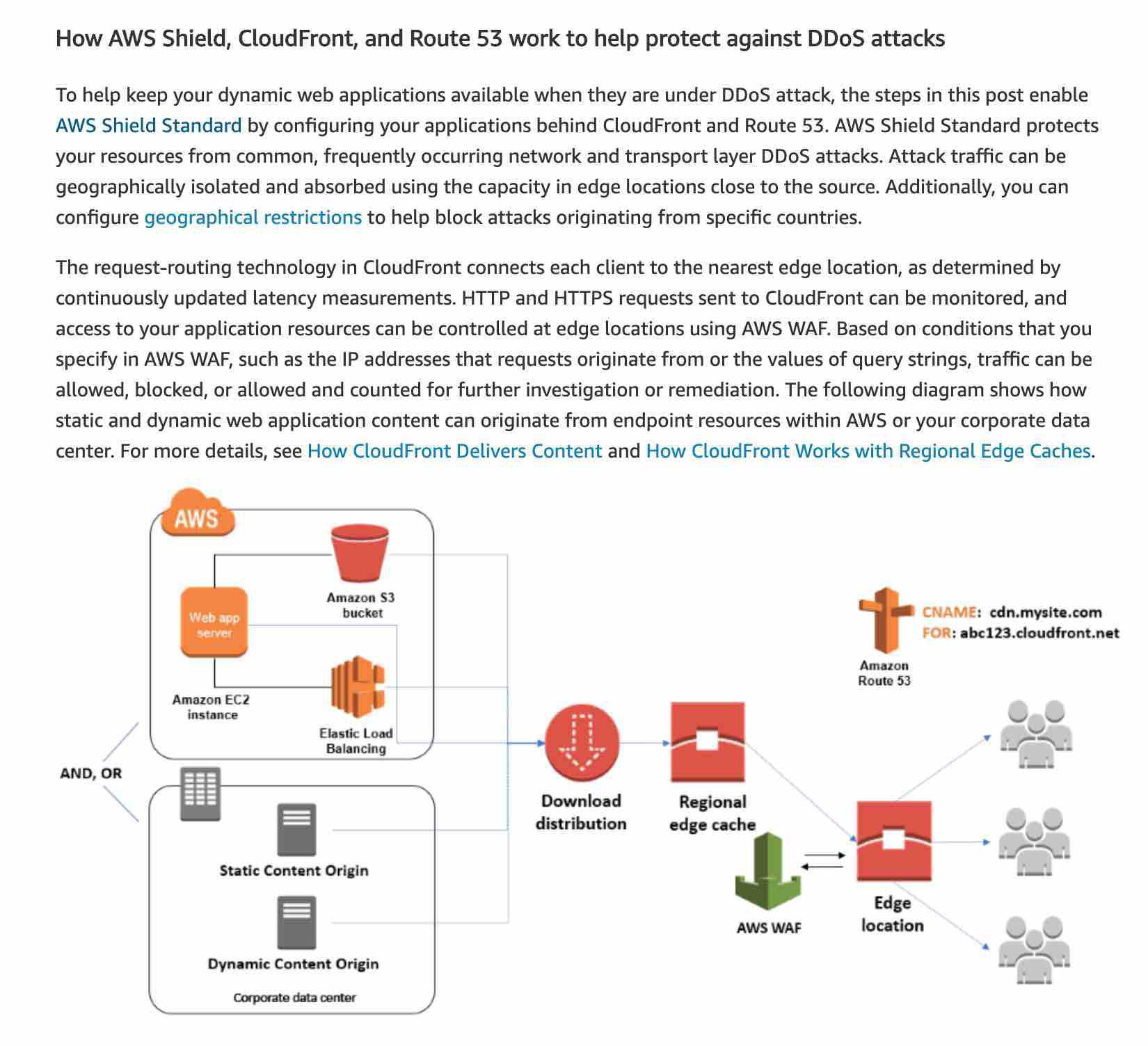
AWS Shield
AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that safeguards applications running on AWS. AWS Shield provides always-on detection and automatic inline mitigations that minimize application downtime and latency, so there is no need to engage AWS Support to benefit from DDoS protection. There are two tiers of AWS Shield - Standard and Advanced.
All AWS customers benefit from the automatic protections of AWS Shield Standard, at no additional charge. AWS Shield Standard defends against most common, frequently occurring network and transport layer DDoS attacks that target your web site or applications. When you use AWS Shield Standard with Amazon CloudFront and Amazon Route 53, you receive comprehensive availability protection against all known infrastructure (Layer 3 and 4) attacks.
For higher levels of protection against attacks targeting your applications running on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon CloudFront, AWS Global Accelerator and Amazon Route 53 resources, you can subscribe to AWS Shield Advanced. In addition to the network and transport layer protections that come with Standard, AWS Shield Advanced provides additional detection and mitigation against large and sophisticated DDoS attacks, near real-time visibility into attacks, and integration with AWS WAF, a web application firewall.
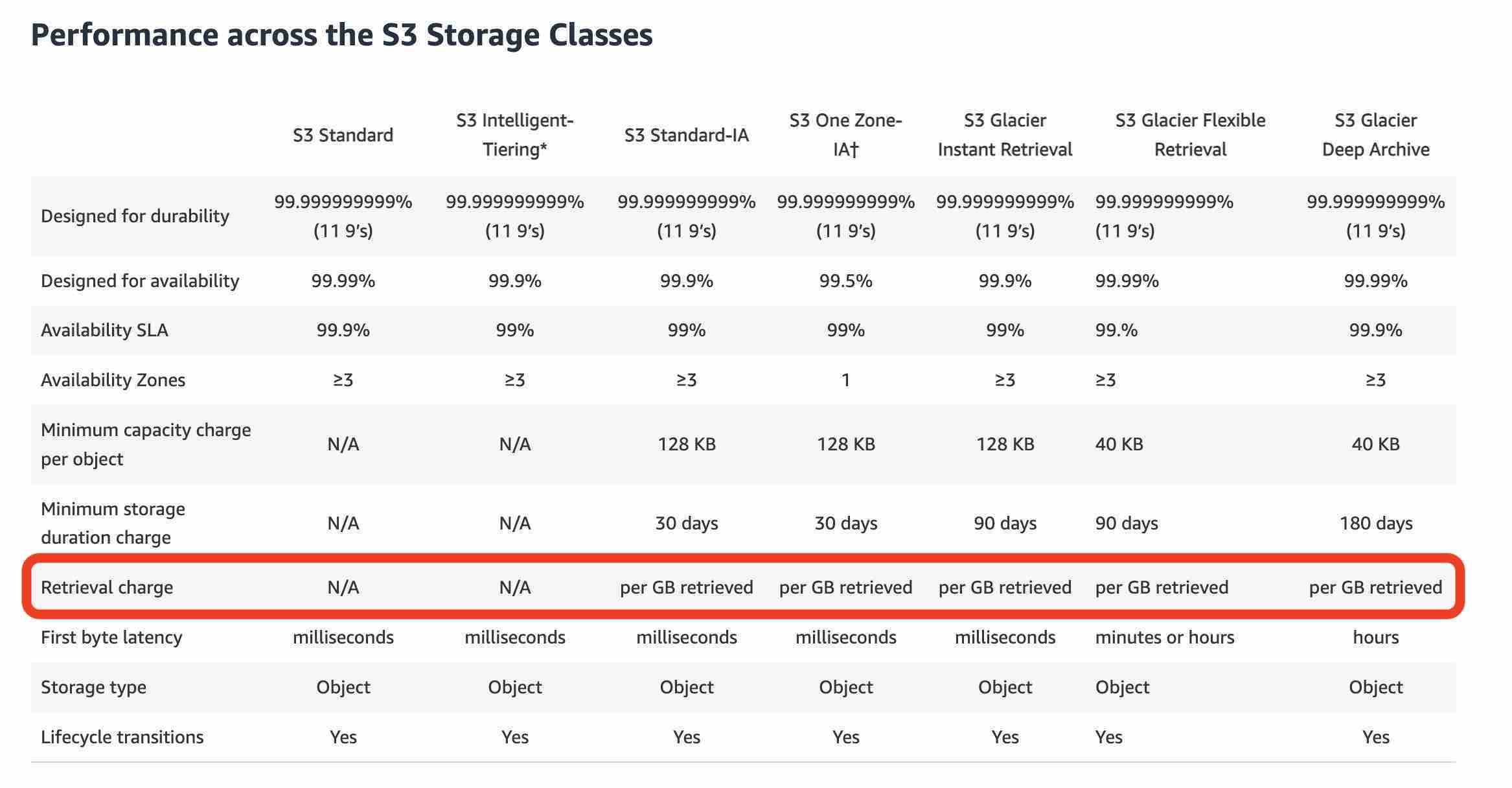
Amazon S3 Storage Classes
https://aws.amazon.com/s3/storage-classes/
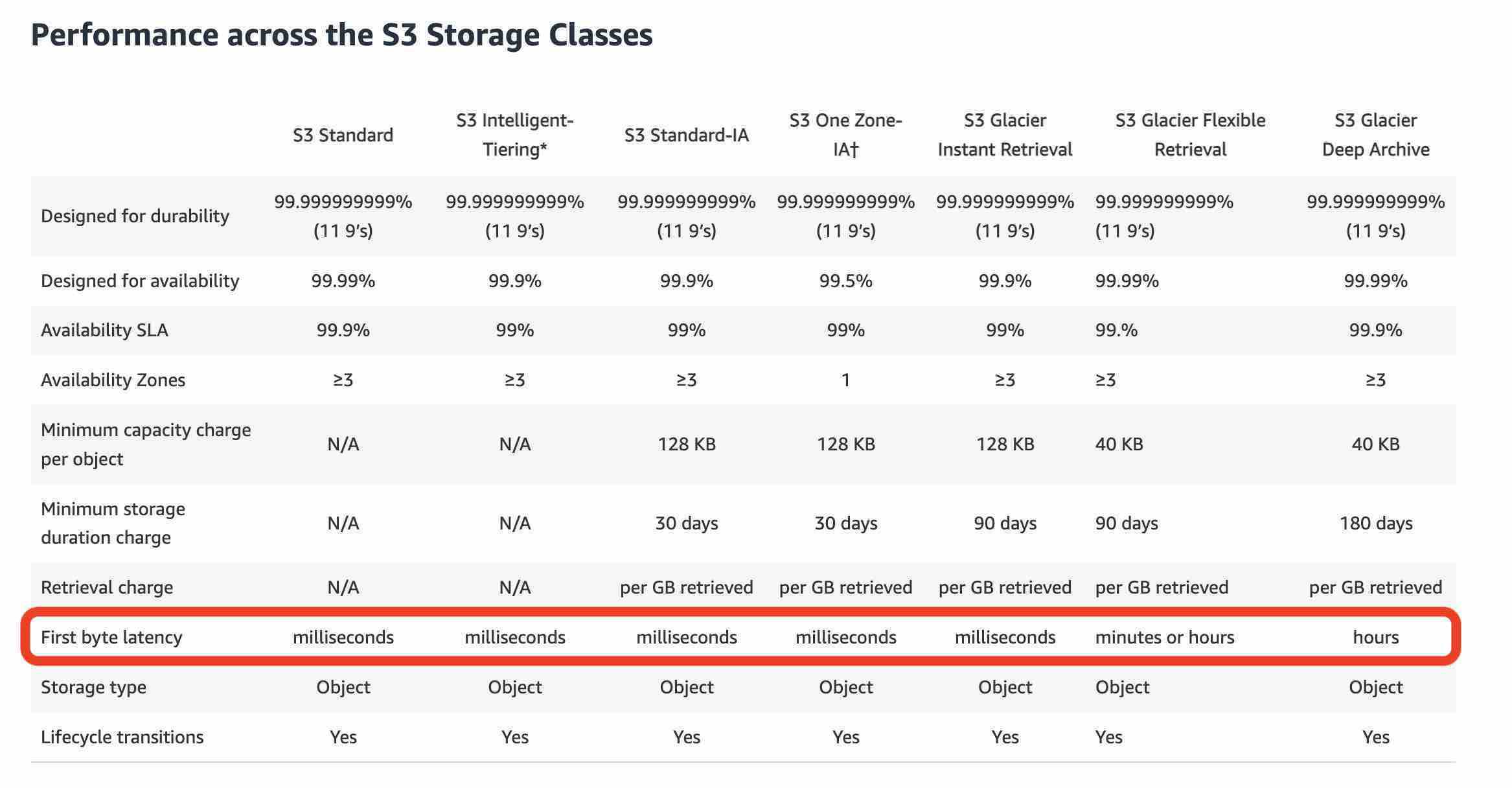
For archive data that does not require immediate access but needs the flexibility to retrieve large sets of data at no cost, such as backup or disaster recovery use cases, choose S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval (formerly S3 Glacier), with retrieval in minutes or free bulk retrievals in 5—12 hours. To save even more on long-lived archive storage such as compliance archives and digital media preservation, choose S3 Glacier Deep Archive, the lowest cost storage in the cloud with data retrieval from 12—48 hours.
Cloudtrail logs are encryption enabled by default… By default, the log files delivered by CloudTrail to your S3 bucket are encrypted using server-side encryption with Amazon S3–managed encryption keys (SSE-S3).
Client-side Encryption for s3
- Use a CMK (customer master key) stored in AWS KMS (Key Management Service)
- Use a Customer provided master key stored in the customer’s proprietary application
Server-side Encryption
-
**Use Amazon S3-managed keys (SSE-S3)**In this, the key material and the key will be provided by AWS itself to encrypt the objects in the S3 bucket.
-
**Use CMK (Customer Master key) in AWS KMS (SSE-KMS)**In this, key material and the key will be generated in AWS KMS service to encrypt the objects in S3 bucket.
-
**Use a Customer provided encryption key (SSE-C)**In this, the key will be provided by the customer and Amazon S3 manages the encryption and decryption process while uploading/downloading the objects into the S3 bucket.
You may see a question around this concept in the exam. Just remember that only S3 and DynamoDB support VPC Endpoint Gateway. All other services that support VPC Endpoints use a VPC Endpoint Interface.
SQS - Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. Using SQS, you can send, store, and receive messages between software components at any volume, without losing messages or requiring other services to be available.
SNS - Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) is a highly available, durable, secure, fully managed pub/sub messaging service that enables you to decouple microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. Using Amazon SNS topics, your publisher systems can fan-out messages to a large number of subscriber endpoints for parallel processing, including Amazon SQS queues, AWS Lambda functions, and HTTP/S webhooks. Additionally, SNS can be used to fan out notifications to end users using mobile push, SMS, and email.
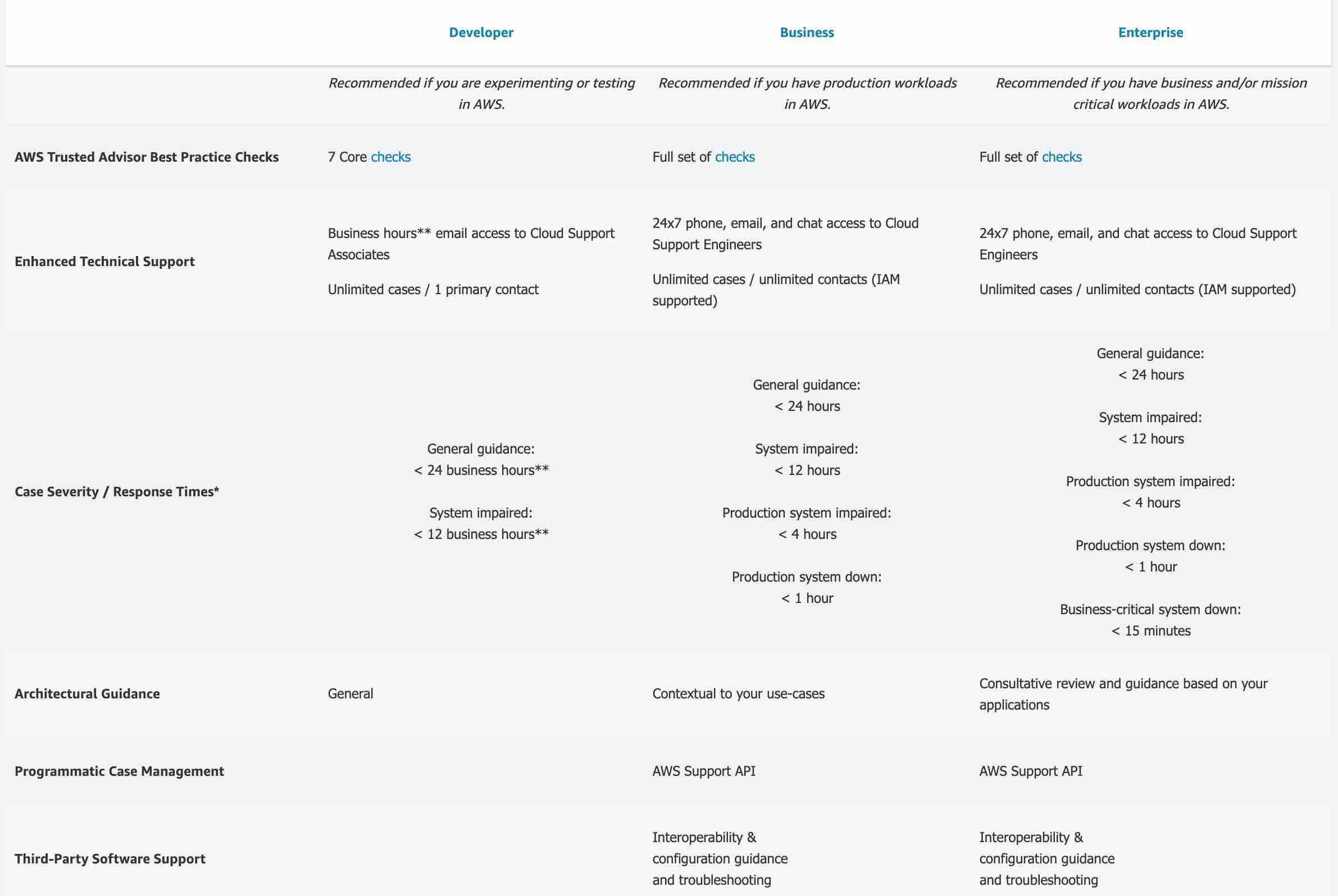
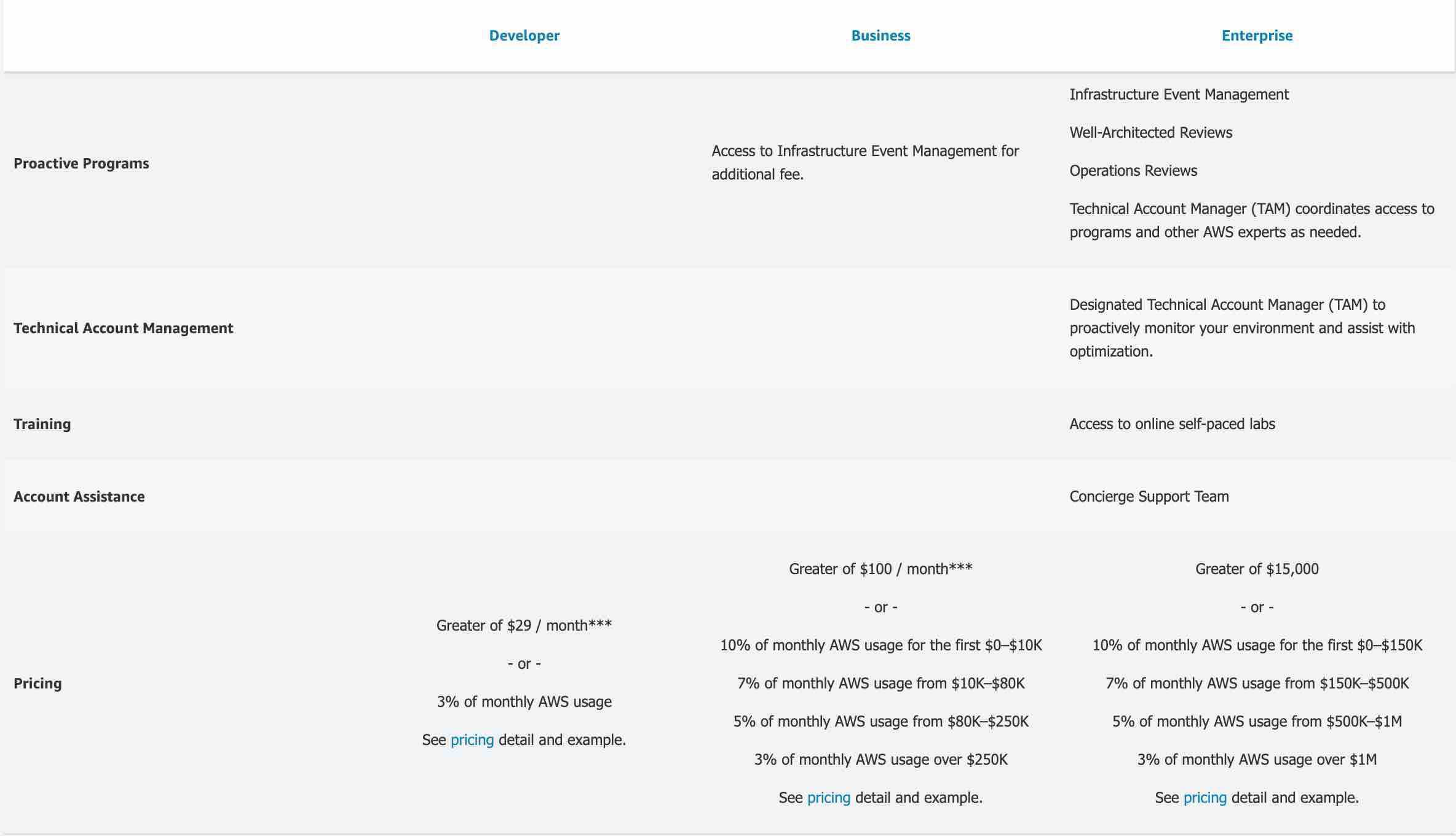
Business - AWS recommends Business Support if you have production workloads on AWS and want 24x7 phone, email and chat access to technical support and architectural guidance in the context of your specific use-cases. You get full access to AWS Trusted Advisor Best Practice Checks. Also, you get access to Infrastructure Event Management for an additional fee.
Developer - AWS recommends Developer Support if you are testing or doing early development on AWS and want the ability to get email-based technical support during business hours as well as general architectural guidance as you build and test.
Basic - The basic plan only provides access to the following:
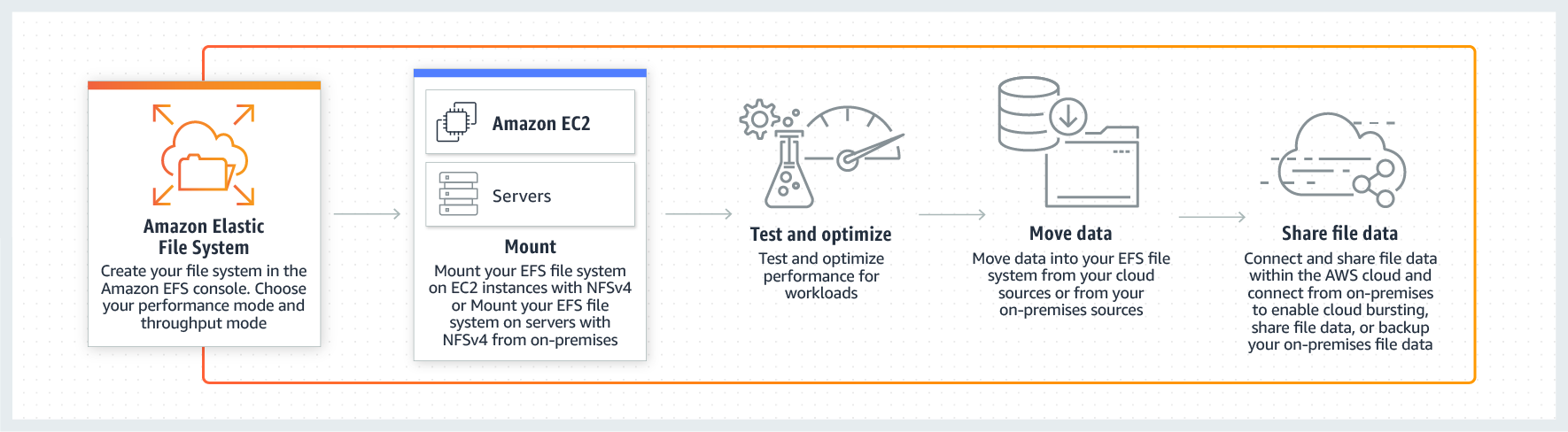
Customer Service & Communities - 24x7 access to customer service, documentation, whitepapers, and support forums. AWS Trusted Advisor - Access to the 7 cEFS” - Amazon EFS is a file storage service for use with Amazon EC2. Amazon EFS provides a file system interface, file system access semantics, and concurrently-accessible storage for up to thousands of Amazon EC2 instances. Amazon EFS uses the Network File System protocol.
How EFS works:esources following best practices to increase performance and improve security. AWS Health - Your Account Health Dashboard : A personalized view of the health of your AWS services, and alerts when your resources are impacted.
Enterprise - AWS Enterprise Support provides customers with concierge-like service where the main focus is helping the customer achieve their outcomes and find success in the cloud. With Enterprise Support, you get 24x7 technical support from high-quality engineers, tools and technology to automatically manage the health of your environment, consultative architectural guidance delivered in the context of your applications and use-cases, and a designated Technical Account Manager (TAM) to coordinate access to proactive/preventative programs and AWS subject matter experts. Access to Infrastructure Event Management is included in the plan.
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/plans/
EFS” - Amazon EFS is a file storage service for use with Amazon EC2. Amazon EFS provides a file system interface, file system access semantics, and concurrently-accessible storage for up to thousands of Amazon EC2 instances. Amazon EFS uses the Network File System protocol.
How EFS works:
Amazon GuardDuty - Amazon GuardDuty is a threat detection service that monitors malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect your AWS account. GuardDuty analyzes billions of events across your AWS accounts from AWS CloudTrail (AWS user and API activity in your accounts), Amazon VPC Flow Logs (network traffic data), and DNS Logs (name query patterns). This service is for AWS account level access, not for instance-level management like an EC2. GuardDuty cannot be used to check OS vulnerabilities.
Amazon Macie - Amazon Macie is a fully managed data security and data privacy service that uses machine learning and pattern matching to discover and protect your sensitive data in AWS. Macie helps identify and alert you to sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII). This service is for securing data and has nothing to do with an EC2 security assessment. Macie cannot be used to check OS vulnerabilities.
AWS Direct Connect
AWS Direct Connect is a cloud service solution that makes it easy to establish a dedicated network connection from your premises to AWS. You can use AWS Direct Connect to establish a private virtual interface from your on-premise network directly to your Amazon VPC, providing you with a private, high bandwidth network connection between your network and your VPC. This connection is private and does not go over the public internet. It takes at least a month to establish this physical connection.
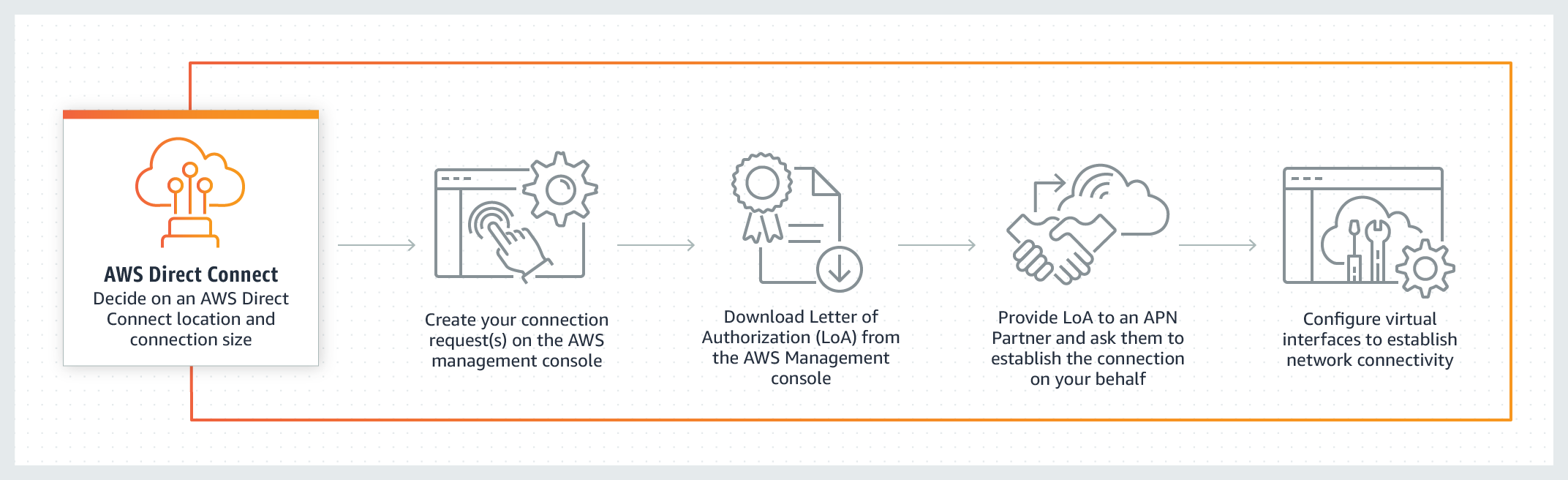
Amazon VPC Endpoint - A VPC endpoint enables you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by AWS PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection. Instances in your VPC do not require public IP addresses to communicate with resources in the service. Traffic between your VPC and the other service does not leave the Amazon network. VPC Endpoint cannot be used to privately connect on-premises data center to AWS Cloud.
Each AWS Region consists of a minimum of three Availability Zones
Each Availability Zone (AZ) consists of one or more discrete data centers
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances let you take advantage of unused EC2 capacity in the AWS cloud. Spot Instances are available at up to a 90% discount compared to On-Demand prices. You can use Spot Instances for various stateless, fault-tolerant, or flexible applications such as big data, containerized workloads, CI/CD, web servers, high-performance computing (HPC), and other test & development workloads
AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) offers protection from common web exploits at which layer? Layer 7
AWS WAF is a web application firewall that lets you monitor the HTTP and HTTPS requests that are forwarded to an Amazon API Gateway API, Amazon CloudFront or an Application Load Balancer. HTTP and HTTPS requests are part of the Application layer, which is layer 7.
Incorrect options:
Layer 3 - Layer 3 is the Network layer and this layer decides which physical path data will take when it moves on the network. AWS Shield offers protection at this layer. WAF does not offer protection at this layer.
Layer 4 - Layer 4 is the Transport layer and this layer data transmission occurs using TCP or UDP protocols. AWS Shield offers protection at this layer. WAF does not offer protection at this layer.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) one example is ec2
AWS Shield Advanced provides expanded DDoS attack protection for web applications running on which of the following resources? (Select two)
Amazon Route 53
AWS Global Accelerator
AWS Shield Standard is activated for all AWS customers, by default. For higher levels of protection against attacks, you can subscribe to AWS Shield Advanced. With Shield Advanced, you also have exclusive access to advanced, real-time metrics and reports for extensive visibility into attacks on your AWS resources. With the assistance of the DRT (DDoS response team), AWS Shield Advanced includes intelligent DDoS attack detection and mitigation for not only for network layer (layer 3) and transport layer (layer 4) attacks but also for application layer (layer 7) attacks.
AWS Shield Advanced provides expanded DDoS attack protection for web applications running on the following resources: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Route 53, AWS Global Accelerator. AWS Global Accelerator is a service in which you create accelerators to improve the performance of your applications for local and global users. Depending on the type of accelerator you choose, you can gain additional benefits:
-
With a standard accelerator, you can improve availability of your internet applications that are used by a global audience. With a standard accelerator, Global Accelerator directs traffic over the AWS global network to endpoints in the nearest Region to the client.
-
With a custom routing accelerator, you can map one or more users to a specific destination among many destinations.
Compute Optimizer - AWS Compute Optimizer recommends optimal AWS resources for your workloads to reduce costs and improve performance by using machine learning to analyze historical utilization metrics. Over-provisioning resources can lead to unnecessary infrastructure costs, and under-provisioning resources can lead to poor application performance. Compute Optimizer helps you choose optimal configurations for three types of AWS resources: Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon EBS volumes, and AWS Lambda functions, based on your utilization data.
Compute Optimizer recommends up to 3 options from 140+ EC2 instance types, as well as a wide range of EBS volume and Lambda function configuration options, to right-size your workloads. Compute Optimizer also projects what the CPU utilization, memory utilization, and run time of your workload would have been on recommended AWS resource options. This helps you understand how your workload would have performed on the recommended options before implementing the recommendations.
How Compute Optimizer works: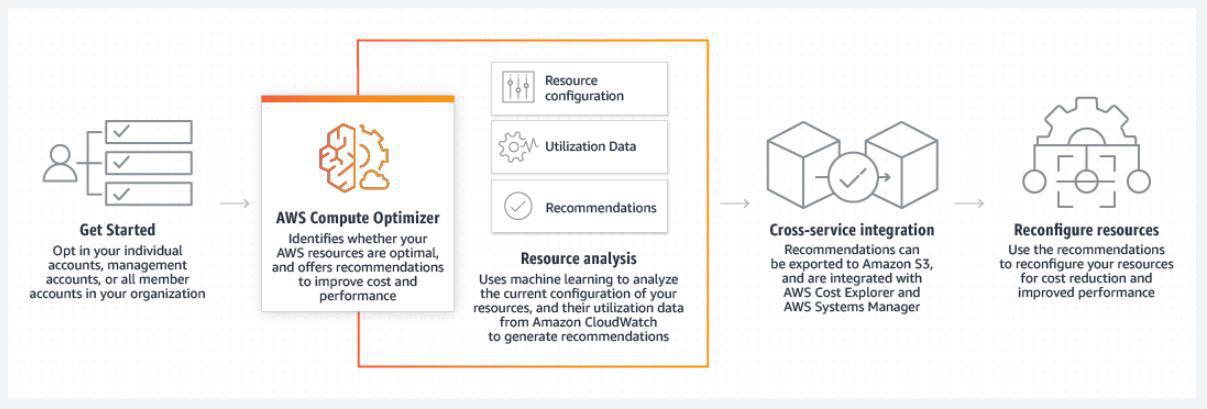
AWS Budgets - AWS Budgets allows you to set custom budgets to track your cost and usage from the simplest to the most complex use cases. With AWS Budgets, you can choose to be alerted by email or SNS notification when actual or forecasted cost and usage exceed your budget threshold, or when your actual RI and Savings Plans’ utilization or coverage drops below your desired threshold. With AWS Budget Actions, you can also configure specific actions to respond to cost and usage status in your accounts, so that if your cost or usage exceeds or is forecasted to exceed your threshold, actions can be executed automatically or with your approval to reduce unintentional over-spending.
AWS Cost Explorer - AWS Cost Explorer has an easy-to-use interface that lets you visualize, understand, and manage your AWS costs and usage over time. Cost Explorer Resource Rightsizing Recommendations and Compute Optimizer use the same recommendation engine. The Compute Optimizer recommendation engine delivers recommendations to help customers identify optimal EC2 instance types for their workloads. The Cost Explorer console and API surface a subset of these recommendations that may lead to cost savings, and augments them with customer-specific cost and savings information (e.g. billing information, available credits, RI, and Savings Plans) to help Cost Management owners quickly identify savings opportunities through infrastructure rightsizing. Compute Optimizer console and its API delivers all recommendations regardless of the cost implications.
Route 53 Routing Policy

Supported aws reservation to optimize cost
EC2 Instances
DynamoDB
RDS
The following AWS services support reservations to optimize costs:
Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances: You can use Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances to reserve capacity and receive a discount on your instance usage compared to running On-Demand instances.
Amazon DynamoDB Reserved Capacity: If you can predict your need for Amazon DynamoDB read-and-write throughput, Reserved Capacity offers significant savings over the normal price of DynamoDB provisioned throughput capacity.
Amazon ElastiCache Reserved Nodes: Amazon ElastiCache Reserved Nodes give you the option to make a low, one-time payment for each cache node you want to reserve and, in turn, receive a significant discount on the hourly charge for that node.
Amazon RDS RIs: Like Amazon EC2 RIs, Amazon RDS RIs can be purchased using No Upfront, Partial Upfront, or All Upfront terms. All Reserved Instance types are available for Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server database engines.
Amazon Redshift Reserved Nodes: If you intend to keep an Amazon Redshift cluster running continuously for a prolonged period, you should consider purchasing reserved-node offerings. These offerings provide significant savings over on-demand pricing, but they require you to reserve compute nodes and commit to paying for those nodes for either a 1- or 3-year duration.
EBS volume can be attached to a single instance in the same Availability Zone whereas EFS file system can be mounted on instances across multiple Availability Zones
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a simple, scalable, fully managed elastic NFS file system for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. It is built to scale on-demand to petabytes without disrupting applications, growing and shrinking automatically as you add and remove files, eliminating the need to provision and manage capacity to accommodate growth.
The service is designed to be highly scalable, highly available, and highly durable. Amazon EFS file systems store data and metadata across multiple Availability Zones in an AWS Region. EFS file system can be mounted on instances across multiple Availability Zones.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is an easy to use, high-performance block storage service designed for use with Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for both throughput and transaction-intensive workloads at any scale.
Designed for mission-critical systems, EBS volumes are replicated within an Availability Zone (AZ) and can easily scale to petabytes of data. You can attach an available EBS volume to one instance that is in the same Availability Zone as the volume.
AWS Artifact
AWS Artifact is your go-to, central resource for compliance-related information that matters to your organization. It provides on-demand access to AWS’ security and compliance reports and select online agreements. Reports available in AWS Artifact include our Service Organization Control (SOC) reports, Payment Card Industry (PCI) reports, and certifications from accreditation bodies across geographies and compliance verticals that validate the implementation and operating effectiveness of AWS security controls. Different types of agreements are available in AWS Artifact Agreements to address the needs of customers subject to specific regulations. For example, the Business Associate Addendum (BAA) is available for customers that need to comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It is not a service, it’s a no-cost, self-service portal for on-demand access to AWS’ compliance reports.
Customer Managed CMK
A customer master key (CMK) is a logical representation of a master key. The CMK includes metadata, such as the key ID, creation date, description, and key state. The CMK also contains the key material used to encrypt and decrypt data. These are created and managed by the AWS customer. Access to these can be controlled using the AWS IAM service.
Incorrect options:
Secrets Manager - AWS Secrets Manager helps you protect secrets needed to access your applications, services, and IT resources. The service enables you to easily rotate, manage, and retrieve database credentials, API keys, and other secrets throughout their lifecycle. You cannot use Secrets Manager for creating and using your own keys for encryption on AWS services.
AWS Managed CMK - AWS managed CMKs are CMKs in your account that are created, managed, and used on your behalf by an AWS service that is integrated with AWS KMS.
AWS Owned CMK - AWS owned CMKs are a collection of CMKs that an AWS service owns and manages for use in multiple AWS accounts. AWS owned CMKs are not in your AWS account. You cannot view or manage these CMKs.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/concepts.html#master_keys
Use Access Key ID and Secret Access Key to access AWS resources programmatically
Access keys are long-term credentials for an IAM user or the AWS account root user. You can use access keys to sign programmatic requests to the AWS CLI or AWS API (directly or using the AWS SDK). Access keys consist of two parts: an access key ID and a secret access key. As a user name and password, you must use both the access key ID and secret access key together to authenticate your requests. When you create an access key pair, save the access key ID and secret access key in a secure location. The secret access key is available only at the time you create it. If you lose your secret access key, you must delete the access key and create a new one.
Amazon DynamoDB with global tables
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed, serverless, key-value NoSQL database designed to run high-performance applications at any scale. DynamoDB offers built-in security, continuous backups, automated multi-region replication, in-memory caching, and data export tools.
DynamoDB global tables replicate data automatically across your choice of AWS Regions and automatically scale capacity to accommodate your workloads. With global tables, your globally distributed applications can access data locally in the selected regions to get single-digit millisecond read and write performance. DynamoDB offers active-active cross-region support that is needed for the company.
AWS Pricing Calculator
AWS Pricing Calculator lets you explore AWS services and create an estimate for the cost of your use cases on AWS. You can model your solutions before building them, explore the price points and calculations behind your estimate, and find the available instance types and contract terms that meet your needs. This enables you to make informed decisions about using AWS. You can plan your AWS costs and usage or price out setting up a new set of instances and services. AWS Pricing Calculator can provide the estimate of the AWS service usage based on the list of AWS services.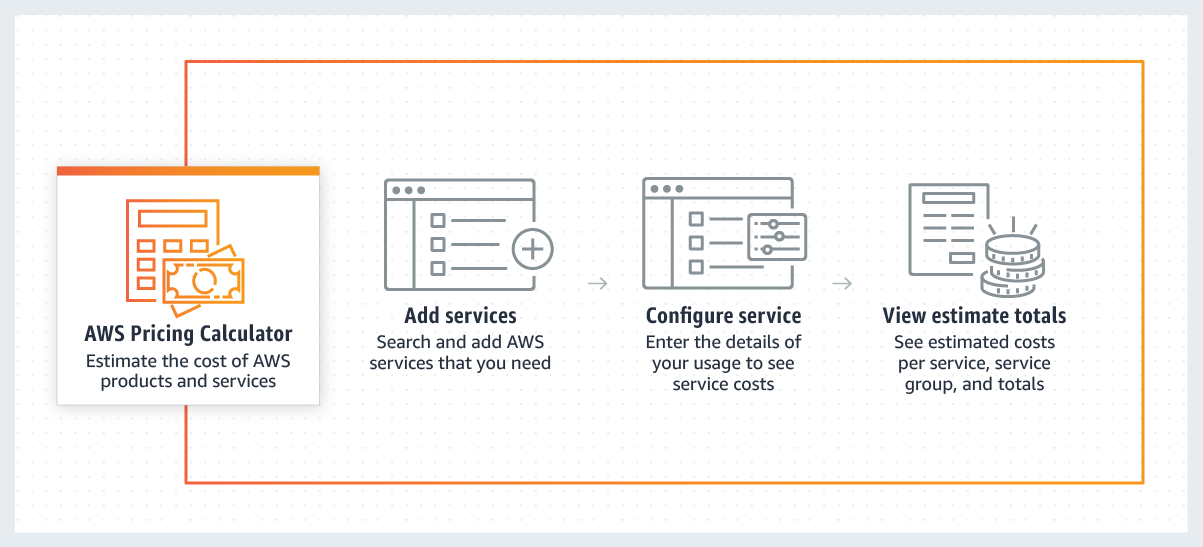


The AWS Partner Network (APN) is the global partner program for technology and consulting businesses that leverage Amazon Web Services to build solutions and services for customers.
APN Consulting Partners are professional services firms that help customers of all types and sizes design, architect, build, migrate, and manage their workloads and applications on AWS, accelerating their migration to AWS cloud.

There are three fundamental drivers of cost with AWS: compute, storage, and outbound data transfer. In most cases, there is no charge for inbound data transfer or data transfer between other AWS services within the same region. Outbound data transfer is aggregated across services and then charged at the outbound data transfer rate.
Per AWS pricing, data transfer between S3 and EC2 instances within the same region is not charged, so there would be no data transfer charge for moving 500 GB of data from an EC2 instance to an S3 bucket in the same region.

 NAT Gateway is managed by AWS but NAT Instance is managed by you.
NAT Gateway is managed by AWS but NAT Instance is managed by you.
Leverage AWS Professional Services to accelerate the infrastructure migration
The AWS Professional Services organization is a global team of experts that can help you realize your desired business outcomes when using the AWS Cloud. AWS Professional Services consultants can supplement your team with specialized skills and experience that can help you achieve quick results. Therefore, leveraging AWS Professional Services can accelerate the infrastructure migration for the startup.
Utilize AWS Partner Network (APN) to build a custom solution for this infrastructure migration
The AWS Partner Network (APN) is the global partner program for technology and consulting businesses that leverage Amazon Web Services to build solutions and services for customers. The startup can work with experts from APN to build a custom solution for this infrastructure migration.
Amazon Elastic Container Service - Fargate launch type
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers. It works with both Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). Fargate makes it easy for you to focus on building your applications. Fargate removes the need to provision and manage servers, lets you specify and pay for resources per application, and improves security through application isolation by design. Fargate allocates the right amount of compute, eliminating the need to choose instances and scale cluster capacity. You only pay for the resources required to run your containers, so there is no over-provisioning and paying for additional servers. Fargate runs each task or pod in its kernel providing the tasks and pods their own isolated compute environment. This enables your application to have workload isolation and improved security by design.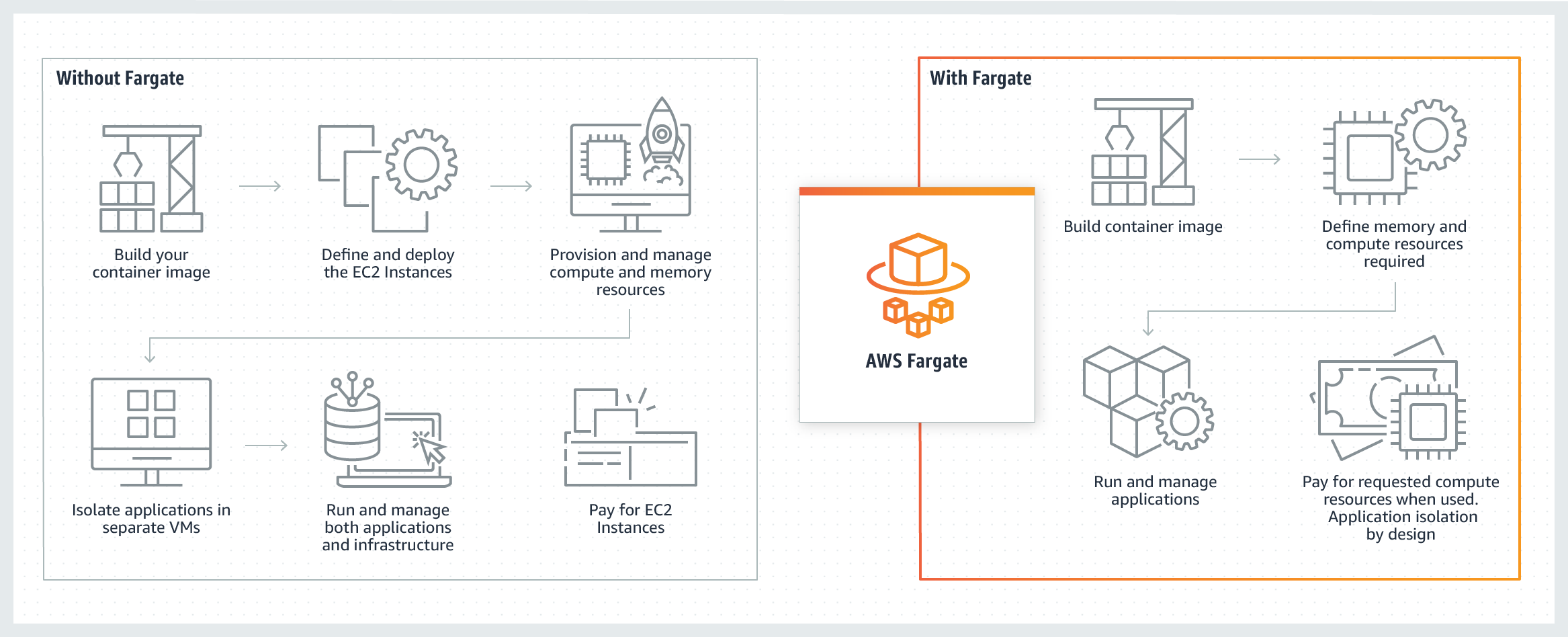
AWS Service Catalog - AWS Service Catalog allows organizations to create and manage catalogs of IT services that are approved for use on AWS. These IT services can include everything from virtual machine images, servers, software, and databases to complete multi-tier application architectures.
AWS Partner Network - Organizations can take help from the AWS Partner Network (APN) to identify the right AWS services to build solutions on AWS Cloud. APN is the global partner program for technology and consulting businesses that leverage Amazon Web Services to build solutions and services for customers.
A VPC spans all of the Availability Zones in the Region whereas a subnet spans only one Availability Zone in the Region Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) is a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including the selection of your IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. A VPC spans all of the Availability Zones in the Region.
A subnet is a range of IP addresses within your VPC. A subnet spans only one Availability Zone in the Region.

S3 is object based storage, EBS is block based storage and EFS is file based storage
AWS Trusted advisor
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/technology/trusted-advisor/
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/technology/trusted-advisor/
https://aws.amazon.com/rds/features/multi-az/
AWS Step Function - AWS Step Function lets you coordinate multiple AWS services into serverless workflows. You can design and run workflows that stitch together services such as AWS Lambda, AWS Glue and Amazon SageMaker.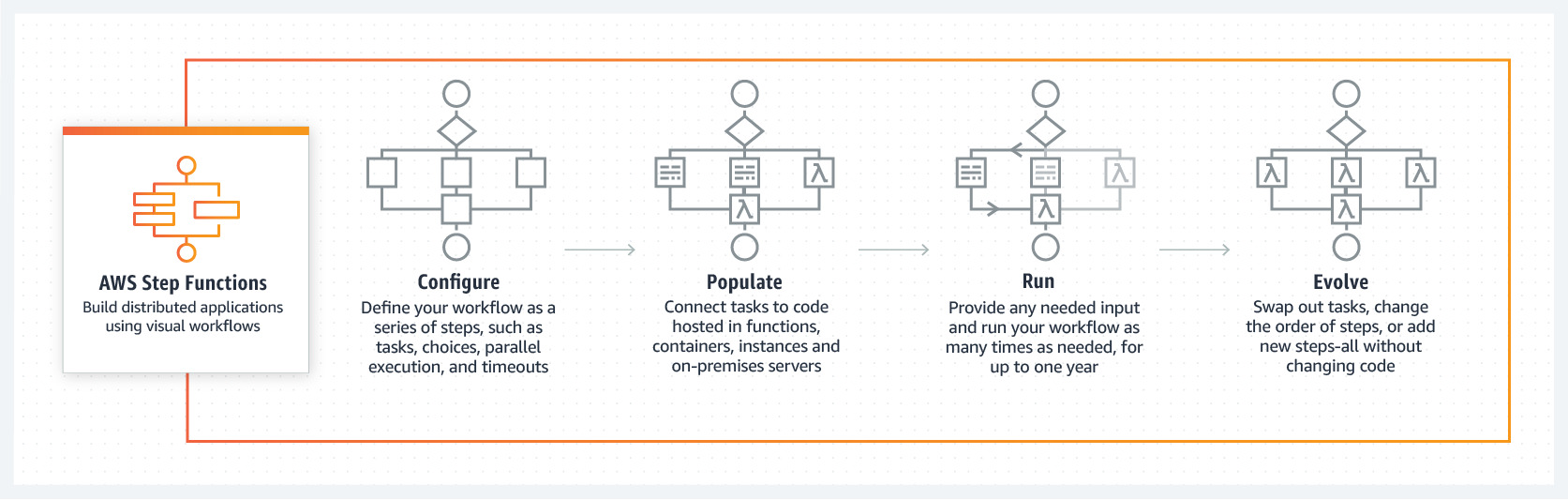 https://aws.amazon.com/step-functions/
https://aws.amazon.com/batch/
https://aws.amazon.com/step-functions/
https://aws.amazon.com/batch/
Understand the difference between AWS Step Functions and AWS Batch. You may get questions to choose one over the other. AWS Batch runs batch computing workloads by provisioning the compute resources. AWS Step Function does not provision any resources. Step Function only orchestrates AWS services required for a given workflow. You cannot use Step Functions to plan, schedule and execute your batch computing workloads by provisioning underlying resources.
https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/
AWS Config
AWS Config is a service that enables you to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of your AWS resources. Config continuously monitors and records your AWS resource configurations and allows you to automate the evaluation of recorded configurations against desired configurations. Think resource-specific history, audit, and compliance; think Config.
With AWS Config, you can do the following: 1. Evaluate your AWS resource configurations for desired settings. 2. Get a snapshot of the current configurations of the supported resources that are associated with your AWS account. 3. Retrieve configurations of one or more resources that exist in your account. 4. Retrieve historical configurations of one or more resources. 5. Receive a notification whenever a resource is created, modified, or deleted. 6.View relationships between resources. For example, you might want to find all resources that use a particular security group.
A photo sharing web application wants to store thumbnails of user-uploaded images on Amazon S3. The thumbnails are rarely used but need to be immediately accessible from the web application. The thumbnails can be regenerated easily if they are lost. Which is the most cost-effective way to store these thumbnails on S3?Use S3 One-Zone Infrequent Access (One-Zone IA) to store the thumbnails
S3 One Zone-IA is for data that is accessed less frequently but requires rapid access when needed. Unlike other S3 Storage Classes which store data in a minimum of three Availability Zones (AZs), S3 One Zone-IA stores data in a single AZ and costs 20% less than S3 Standard-IA. S3 One Zone-IA offers the same high durability, high throughput, and low latency of S3 Standard, with a low per GB storage price and per GB retrieval fee. Although S3 One Zone-IA offers less availability than S3 Standard but that’s not an issue for the given use-case since the thumbnails can be regenerated easily.
As the thumbnails are rarely used but need to be rapidly accessed when required, so S3 One Zone-IA is the best choice for this use-case.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/VPC_SecurityGroups.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/vpc-network-acls.html
AWS Local Zones
AWS Local Zones allow you to use select AWS services, like compute and storage services, closer to more end-users, providing them very low latency access to the applications running locally. AWS Local Zones are also connected to the parent region via Amazon’s redundant and very high bandwidth private network, giving applications running in AWS Local Zones fast, secure, and seamless access to the rest of AWS services.
You should use AWS Local Zones to deploy workloads closer to your end-users for low-latency requirements. AWS Local Zones have their connection to the internet and support AWS Direct Connect, so resources created in the Local Zone can serve local end-users with very low-latency communications.
Various AWS services such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS), Amazon FSx, Amazon Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon EMR, Amazon ElastiCache, and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) are available locally in the AWS Local Zones. You can also use services that orchestrate or work with local services such as Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, Amazon EKS clusters, Amazon ECS clusters, Amazon EC2 Systems Manager, Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, and AWS CloudFormation. AWS Local Zones also provide a high-bandwidth, secure connection to the AWS Region, allowing you to seamlessly connect to the full range of services in the AWS Region through the same APIs and toolsets
AWS Edge Locations - An AWS Edge location is a site that CloudFront uses to cache copies of the content for faster delivery to users at any location.
https://aws.amazon.com/rekognition/
ASG IAM always free
AWS Pillars needs to recap with details.
AWS Systems Manager Session Manager
AWS SSM Session Manager is a fully-managed service that provides you with an interactive browser-based shell and CLI experience. It helps provide secure and auditable instance management without the need to open inbound ports, maintain bastion hosts, and manage SSH keys. Session Manager helps to enable compliance with corporate policies that require controlled access to instances, increase security and auditability of access to the instances while providing simplicity and cross-platform instance access to end-users.
 https://aws.amazon.com/storagegateway/features/
https://aws.amazon.com/storagegateway/features/
The AWS Health - Service Health Dashboard is the single place to learn about the availability and operations of AWS services. You can view the overall status of AWS services, and you can sign in to view personalized communications about your particular AWS account or organization.
You can check on this page https://health.aws.amazon.com/health/status to get current status information.
Aws compute Optimizer
AWS Compute Optimizer helps you identify the optimal AWS resource configurations, such as Amazon EC2 instance types, Amazon EBS volume configurations, and AWS Lambda function memory sizes, using machine learning to analyze historical utilization metrics. AWS Compute Optimizer delivers recommendations for selected types of EC2 instances, EC2 Auto Scaling groups, EBS volumes, and Lambda functions.
Compute Optimizer calculates an individual performance risk score for each resource dimension of the recommended instance, including CPU, memory, EBS throughput, EBS IOPS, disk throughput, disk throughput, network throughput, and network packets per second (PPS).
AWS Compute Optimizer provides EC2 instance type and size recommendations for EC2 Auto Scaling groups with a fixed group size, meaning desired, minimum, and maximum are all set to the same value and have no scaling policy attached.
AWS Compute Optimizer supports IOPS and throughput recommendations for General Purpose (SSD) (gp3) volumes and IOPS recommendations for Provisioned IOPS (io1 and io2) volumes.
Compute Optimizer helps you optimize two categories of Lambda functions. The first category includes Lambda functions that may be over-provisioned in memory sizes. The second category includes compute-intensive Lambda functions that may benefit from additional CPU power.
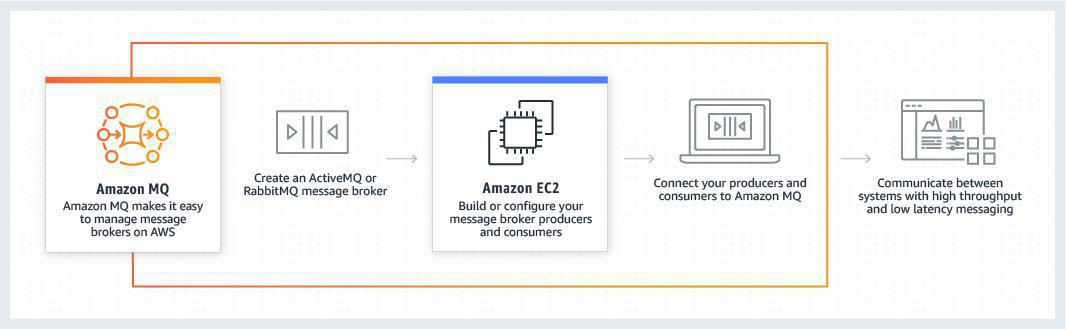
Amazon MQ
- Amazon MQ is a managed message broker service for Apache ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ that makes it easy to set up and operate message brokers on AWS. Amazon MQ reduces your operational responsibilities by managing the provisioning, setup, and maintenance of message brokers for you. Because Amazon MQ connects to your current applications with industry-standard APIs and protocols, you can easily migrate to AWS without having to rewrite code.
If you’re using messaging with existing applications, and want to move the messaging functionality to the cloud quickly and easily, AWS recommends you consider Amazon MQ. It supports industry-standard APIs and protocols so you can switch from any standards-based message broker to Amazon MQ without rewriting the messaging code in your applications. If you are building brand new applications in the cloud, AWS recommends you consider Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS.
How MQ works:
AWS Budget and Cloud watch
via - https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-budgets/
Exam Alert:
It is useful to note the difference between CloudWatch Billing vs Budgets:
CloudWatch Billing Alarms: Sends an alarm when the actual cost exceeds a certain threshold.
Budgets: Sends an alarm when the actual cost exceeds the budgeted amount or even when the cost forecast exceeds the budgeted amount.
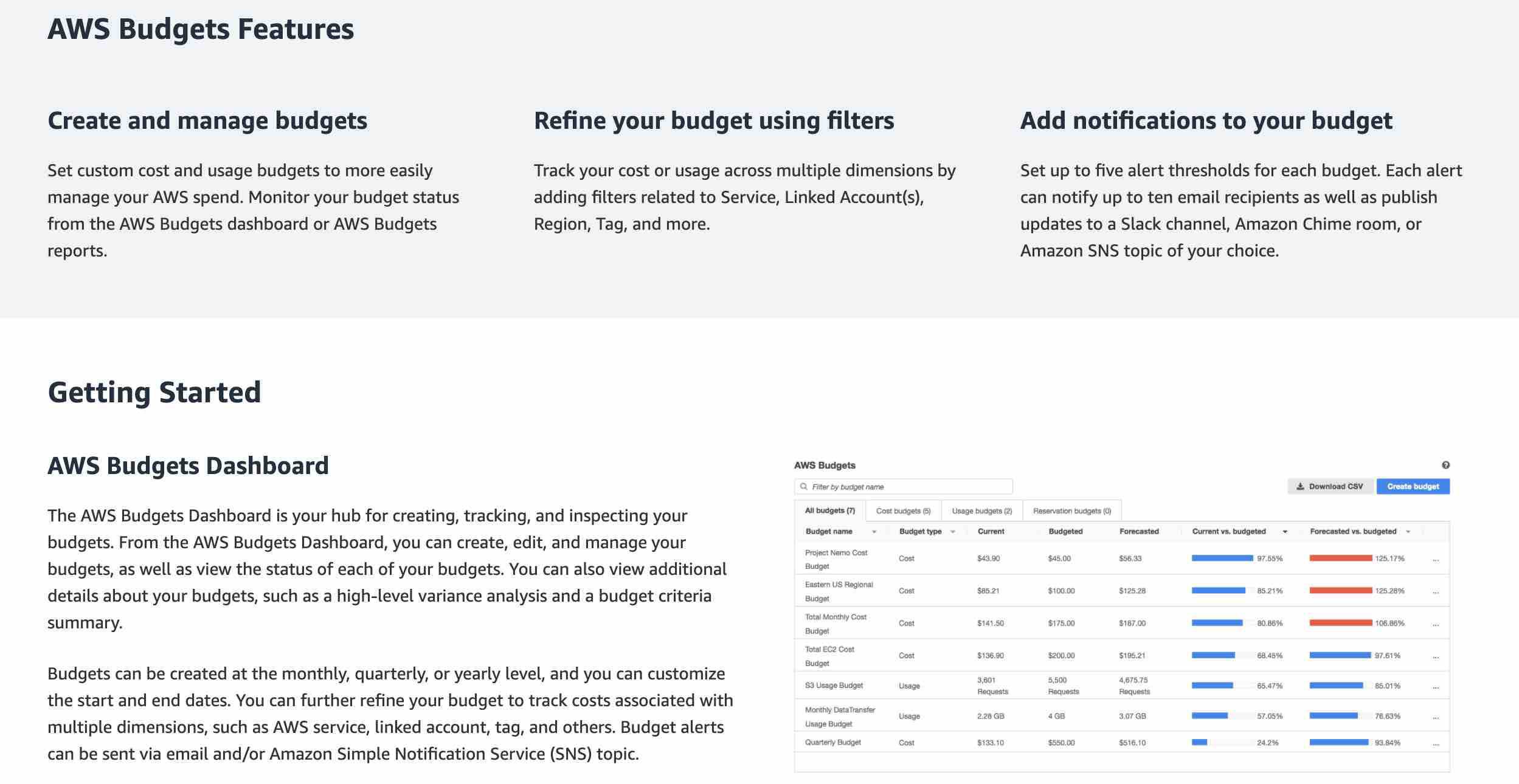 AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets gives the ability to set custom budgets that alert you when your costs or usage exceed (or are forecasted to exceed) your budgeted amount. You can also use AWS Budgets to set reservation utilization or coverage targets and receive alerts when your utilization drops below the threshold you define. Budgets can be created at the monthly, quarterly, or yearly level, and you can customize the start and end dates. You can further refine your budget to track costs associated with multiple dimensions, such as AWS service, linked account, tag, and others. Budget alerts can be sent via email and/or Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) topic.
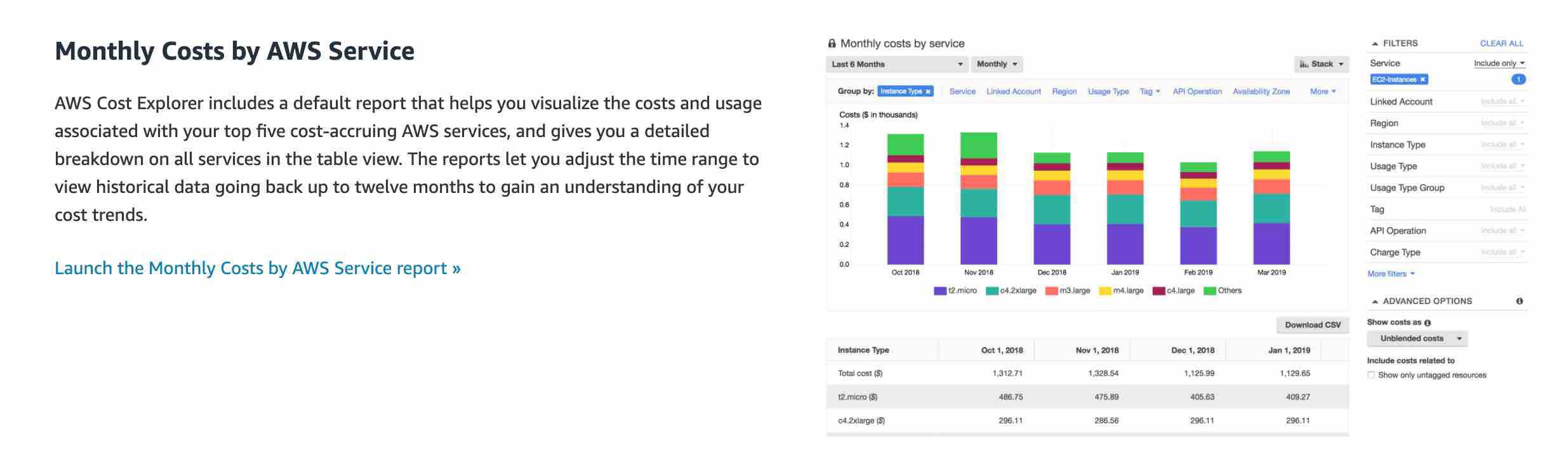
AWS Cost Explorer - AWS Cost Explorer has an easy-to-use interface that lets you visualize, understand, and manage your AWS costs and usage over time. AWS Cost Explorer includes a default report that helps you visualize the costs and usage associated with your top five cost-accruing AWS services, and gives you a detailed breakdown on all services in the table view. The reports let you adjust the time range to view historical data going back up to twelve months to gain an understanding of your cost trends.
AWS Cost Explorer Reports:
IAM Role - An IAM role is similar to an IAM user, in that it is an AWS identity with permission policies that determine what the identity can and cannot do in AWS. However, instead of being uniquely associated with one person, a role is intended to be assumable by anyone who needs it.
IAM Group - An IAM group is a collection of IAM users. Groups let you specify permissions for multiple users, which can make it easier to manage the permissions for those users.
AWS Policy - You manage access in AWS by creating policies and attaching them to IAM identities (users, groups of users, or roles) or AWS resources. A policy is an object in AWS that, when associated with an identity or resource, defines their permissions.
https://d1.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/architecture/AWS_Well-Architected_Framework.pdf
Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration enables fast, easy, and secure transfers of files over long distances between your client and an S3 bucket. Transfer Acceleration takes advantage of Amazon CloudFront’s globally distributed edge locations. As the data arrives at an edge location, data is routed to Amazon S3 over an optimized network path. Transfer Acceleration cannot be used to improve the performance of a static website.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/transfer-acceleration.html
Autoscaling group
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/AutoScalingGroup.html
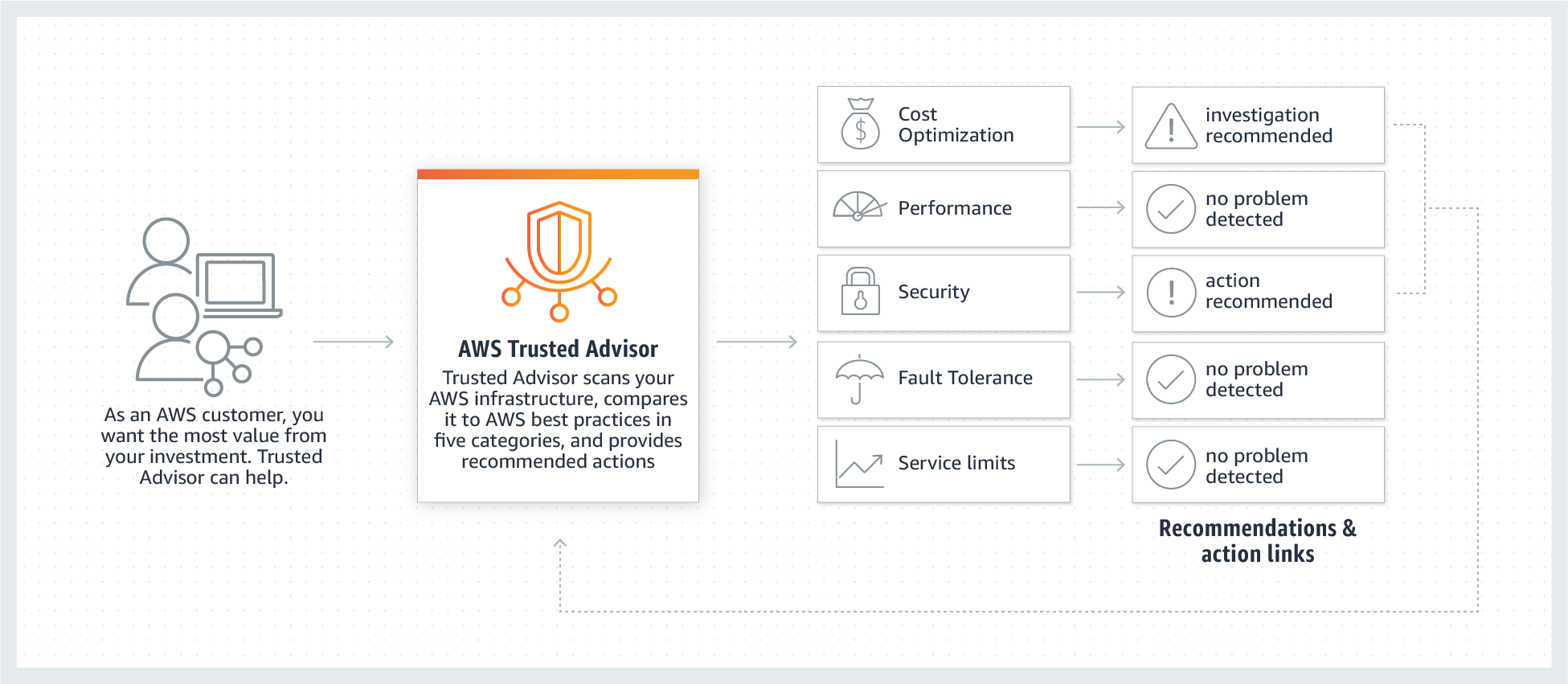
AWS Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor is an online tool that provides real-time guidance to help provision your resources following AWS best practices. Whether establishing new workflows, developing applications, or as part of ongoing improvement, recommendations provided by Trusted Advisor regularly help keep your solutions provisioned optimally. AWS Trusted Advisor analyzes your AWS environment and provides best practice recommendations in five categories: Cost Optimization, Performance, Security, Fault Tolerance, Service Limits.
AWS Trusted Advisor checks the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances that were running at any time during the last 14 days and alerts you if the daily CPU utilization was 10% or less and network I/O was 5 MB or less on 4 or more days. via - https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/technology/trusted-advisor/best-practice-checklist/#Cost_Optimization
AWS Cost Explorer
AWS Cost Explorer has an easy-to-use interface that lets you visualize, understand, and manage your AWS costs and usage over time. AWS Cost Explorer includes a default report that helps you visualize the costs and usage associated with your top five cost-accruing AWS services, and gives you a detailed breakdown of all services in the table view. The reports let you adjust the time range to view historical data going back up to twelve months to gain an understanding of your cost trends.
The rightsizing recommendations feature in Cost Explorer helps you identify cost-saving opportunities by downsizing or terminating EC2 instances. You can see all of your underutilized EC2 instances across member accounts in a single view to immediately identify how much you can save.
via - https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/
“AWS Cost Explorer” vs “AWS Cost and Usage Reports”: 
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-and-usage-reporting/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-and-usage-reporting/
References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cur/latest/userguide/what-is-cur.html
https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/
https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-and-usage-reporting/
NEED TO WORK COST RELATED AWS PRODUCTS.
** Effect, Action - Most policies are stored in AWS as JSON documents. Identity-based policies and policies used to set permissions boundaries are JSON policy documents that you attach to a user or role. Resource-based policies are JSON policy documents that you attach to a resource.
A JSON policy document includes these elements:
- Optional policy-wide information at the top of the document
- One or more individual statements
Each statement includes information about a single permission. The information in a statement is contained within a series of elements.
-
Version – Specify the version of the policy language that you want to use. As a best practice, use the latest 2012-10-17 version.
-
Statement – Use this main policy element as a container for the following elements. You can include more than one statement in a policy.
-
Sid (Optional) – Include an optional statement ID to differentiate between your statements.
-
Effect – Use Allow or Deny to indicate whether the policy allows or denies access.
-
Principal (Required in only some circumstances) – If you create a resource-based policy, you must indicate the account, user, role, or federated user to which you would like to allow or deny access. If you are creating an IAM permissions policy to attach to a user or role, you cannot include this element. The principal is implied as that user or role.
-
Action – Include a list of actions that the policy allows or denies.
-
Resource (Required in only some circumstances) – If you create an IAM permissions policy, you must specify a list of resources to which the actions apply. If you create a resource-based policy, this element is optional. If you do not include this element, then the resource to which the action applies is the resource to which the policy is attached.
-
Condition (Optional) – Specify the circumstances under which the policy grants permission.
-
Amazon EFS Overview:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/efs/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/efs/
DynamoDB - Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It’s a fully managed, multi-Region, multi-master, durable database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications. All of your data is stored on solid-state disks (SSDs) and is automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones in an AWS Region, providing built-in high availability and data durability.
DynamoDB High Availability:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/Introduction.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/Introduction.html
EFS - Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a simple, scalable, fully managed elastic NFS file system for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. It is built to scale on-demand to petabytes without disrupting applications, growing and shrinking automatically as you add and remove files, eliminating the need to provision and manage capacity to accommodate growth. Amazon EFS is a regional service storing data within and across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) for high availability and durability.
EFS High Availability:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/efs/faq/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/efs/faq/
US East (N. Virginia) - us-east-1
You can monitor your estimated AWS charges by using Amazon CloudWatch. Billing metric data is stored in the US East (N. Virginia) Region and represents worldwide charges. This data includes the estimated charges for every service in AWS that you use, in addition to the estimated overall total of your AWS charges.\
You may see a question around this concept in the exam. Just remember that only S3 and DynamoDB support VPC Endpoint Gateway. All other services that support VPC Endpoints use a VPC Endpoint Interface.
Read Replica improves database scalability
Virtual Private Gateway
Customer Gateway
AWS Site-to-Site VPN enables you to securely connect your on-premises network or branch office site to your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC). VPN Connections are a good solution if you have an immediate need, and have low to modest bandwidth requirements. This connection goes over the public internet. Virtual Private Gateway (or a Transit Gateway) and Customer Gateway are the components of a VPC.
A virtual private gateway is the VPN concentrator on the Amazon side of the Site-to-Site VPN connection. A customer gateway is a resource in AWS that provides information to AWS about your Customer gateway device.
Components of an AWS Site-to-Site VPN:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpn/latest/s2svpn/how_it_works.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpn/latest/s2svpn/how_it_works.html
You will pay a fee each time you read from or write data stored on the EFS - Infrequent Access storage class - The Infrequent Access storage class is cost-optimized for files accessed less frequently. Data stored on the Infrequent Access storage class costs less than Standard and you will pay a fee each time you read from or write to a file.
Amazon EBS Snapshots are stored incrementally, which means you are billed only for the changed blocks stored - Amazon EBS Snapshots are a point in time copy of your block data. For the first snapshot of a volume, Amazon EBS saves a full copy of your data to Amazon S3. EBS Snapshots are stored incrementally, which means you are billed only for the changed blocks stored.
You must use an AMI from the same region as that of the EC2 instance. The region of the AMI has no bearing on the performance of the EC2 instance
An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provides the information required to launch an instance. You must specify an AMI when you launch an instance. You can launch multiple instances from a single AMI when you need multiple instances with the same configuration.
The AMI must be in the same region as that of the EC2 instance to be launched. If the AMI exists in a different region, you can copy that AMI to the region where you want to launch the EC2 instance. The region of AMI has no bearing on the performance of the EC2 instance.
Amazon Machine Images (AMI) Overview:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AMIs.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AMIs.html
For each resource, each tag key must be unique, and each tag key can have only one value
You must activate both AWS generated tags and user-defined tags separately before they can appear in Cost Explorer or on a cost allocation report
A Cost Allocation Tag is a label that you or AWS assigns to an AWS resource. Each tag consists of a key and a value. For each resource, each tag key must be unique, and each tag key can have only one value. You can use tags to organize your resources, and cost allocation tags to track your AWS costs on a detailed level.
AWS provides two types of cost allocation tags, an AWS generated tags and user-defined tags. AWS defines, creates, and applies the AWS generated tags for you, and you define, create, and apply user-defined tags. You must activate both types of tags separately before they can appear in Cost Explorer or on a cost allocation report.
AWS Cost Allocation Tags Overview:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/awsaccountbilling/latest/aboutv2/cost-alloc-tags.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/awsaccountbilling/latest/aboutv2/cost-alloc-tags.html
Amazon S3 Glacier - Amazon S3 Glacier (S3 Glacier), is a storage service optimized for infrequently used data, or “cold data. Data at rest stored in S3 Glacier is automatically server-side encrypted using 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256) with keys maintained by AWS.
AWS Storage Gateway - AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid cloud storage service that gives you on-premises access to virtually unlimited cloud storage. All data transferred between the gateway and AWS storage is encrypted using SSL (for all three types of gateways - File, Volume and Tape Gateways).
AWS Migration Evaluator
Migration Evaluator (Formerly TSO Logic) is a complimentary service to create data-driven business cases for AWS Cloud planning and migration.
Migration Evaluator quickly provides a business case to make sound AWS planning and migration decisions. With Migration Evaluator, your organization can build a data-driven business case for AWS, gets access to AWS expertise, visibility into the costs associated with multiple migration strategies, and insights on how reusing existing software licensing reduces costs further.
AWS Shield Advanced offers protection against higher fees that could result from a DDoS attack
AWS Shield Advanced offers some cost protection against spikes in your AWS bill that could result from a DDoS attack. This cost protection is provided for your Elastic Load Balancing load balancers, Amazon CloudFront distributions, Amazon Route 53 hosted zones, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud instances, and your AWS Global Accelerator accelerators.
AWS Shield Advanced is a paid service for all customers, irrespective of the Support plan.
Amazon Kendra - Amazon Kendra is an intelligent search service powered by machine learning. Kendra reimagines enterprise search for your websites and applications so your employees and customers can easily find the content they are looking for, even when it’s scattered across multiple locations and content repositories within your organization.
Using Amazon Kendra, you can stop searching through troves of unstructured data and discover the right answers to your questions, when you need them. Amazon Kendra is a fully managed service, so there are no servers to provision, and no machine learning models to build, train, or deploy. Kendra supports unstructured and semi-structured data in .html, MS Office (.doc, .ppt), PDF, and text formats.
Unlike conventional search technology, natural language search capabilities return the answers you’re looking for quickly and accurately, no matter where the information lives within your organization.
Kendra’s deep learning models come pre-trained across 14 industry domains, allowing it to extract more accurate answers across a wide range of business use cases from the get-go. You can also fine-tune search results by manually adjusting the importance of data sources, authors, freshness, or using custom tags.
Incorrect options:
Amazon Personalize - Amazon Personalize enables developers to build applications with the same machine learning (ML) technology used by Amazon.com for real-time personalized recommendations. Amazon Personalize makes it easy for developers to build applications capable of delivering a wide array of personalization experiences, including specific product recommendations, personalized product re-ranking, and customized direct marketing.
Amazon Comprehend - Amazon Comprehend is a natural-language processing (NLP) service that uses machine learning to uncover information in unstructured data. Instead of combing through documents, the process is simplified and unseen information is easier to understand.
Amazon Kendra provides ML-powered search capabilities for all unstructured data customers store in AWS. Kendra offers easy-to-use native connectors to popular AWS repository types such as S3 and RDS databases. Other AI services such as Amazon Comprehend, Amazon Transcribe, and Amazon Comprehend Medical can be used to pre-process documents, generate searchable text, extract entities, and enrich their metadata for more specialized search experiences.
Amazon Lex - Amazon Lex is a service for building conversational interfaces into any application using voice and text. Amazon Lex provides the advanced deep learning functionalities of automatic speech recognition (ASR) for converting speech to text, and natural language understanding (NLU) to recognize the intent of the text, to enable you to build applications with highly engaging user experiences and lifelike conversational interactions.
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/kendra/
**The company should just start creating new resources in the destination AWS Region and then migrate the relevant data and applications into this new AWS Region** - The company needs to create resources in the new AWS Region and then move the relevant data and applications into the new AWS Region. There is no off-the-shelf solution or service that the company can use to facilitate this transition.The company should just start creating new resources in the destination AWS Region and then migrate the relevant data and applications into this new AWS Region - The company needs to create resources in the new AWS Region and then move the relevant data and applications into the new AWS Region. There is no off-the-shelf solution or service that the company can use to facilitate this transition.
WS Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway connects VPCs and on-premises networks through a central hub. This simplifies your network and puts an end to complex peering relationships. It acts as a cloud router – each new connection is only made once. As you expand globally, inter-Region peering connects AWS Transit Gateways using the AWS global network. Your data is automatically encrypted and never travels over the public internet.
How Transit Gateway can simplify your network:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/transit-gateway/
VPC Peering - A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them privately. VPC peering is not transitive, a separate VPC peering connection has to be made between two VPCs that need to talk to each other. With growing VPCs, this gets difficult to manage.
via - https://aws.amazon.com/transit-gateway/
VPC Peering - A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them privately. VPC peering is not transitive, a separate VPC peering connection has to be made between two VPCs that need to talk to each other. With growing VPCs, this gets difficult to manage.
Transitive VPC Peering is not allowed: 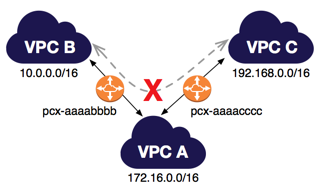 via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/peering/invalid-peering-configurations.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/peering/invalid-peering-configurations.html
Use Cross-Region replication (CRR) to replicate data between distant AWS Regions
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance.
Replication enables automatic, asynchronous copying of objects across Amazon S3 buckets. Buckets that are configured for object replication can be owned by the same AWS account or by different accounts. You can copy objects between different AWS Regions or within the same Region.
Although Amazon S3 stores your data across multiple geographically distant Availability Zones by default, compliance requirements might dictate that you store data at even greater distances. Cross-Region Replication (CRR) allows you to replicate data between distant AWS Regions to satisfy these requirements.
Incorrect options:
Use Same-Region replication (SRR) to replicate data between distant AWS Regions - SRR is used to copy objects across Amazon S3 buckets in the same AWS Region, so this option is incorrect.
Exam Alert:
Please review the differences between SRR and CRR:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/replication.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/replication.html
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined.
The following are the key concepts for VPCs:
Virtual private cloud (VPC) — A virtual network dedicated to your AWS account.
Subnet — A range of IP addresses in your VPC.
Route table — A set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic is directed.
Internet Gateway — A gateway that you attach to your VPC to enable communication between resources in your VPC and the internet.
VPC endpoint — Enables you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/awsaccountbilling/latest/aboutv2/consolidatedbilling-other.html
AZ is One or more data centers in the same location

There are four cost components to consider for S3 pricing – storage pricing; request and data retrieval pricing; data transfer and transfer acceleration pricing; and data management features pricing. Under “Data Transfer”, You pay for all bandwidth into and out of Amazon S3, except for the following: (1) Data transferred in from the internet, (2) Data transferred out to an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance, when the instance is in the same AWS Region as the S3 bucket, (3) Data transferred out to Amazon CloudFront (CloudFront).
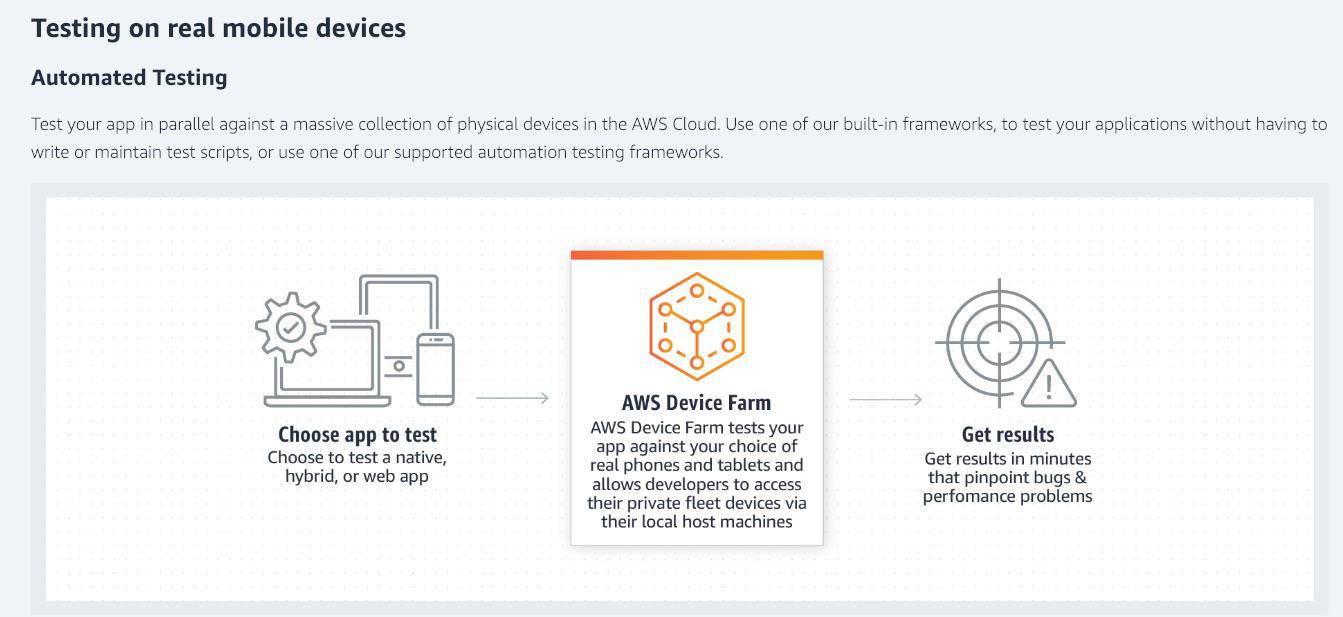
AWS Device Farm
- AWS Device Farm is an application testing service that lets you improve the quality of your web and mobile apps by testing them across an extensive range of desktop browsers and real mobile devices; without having to provision and manage any testing infrastructure. The service enables you to run your tests concurrently on multiple desktop browsers or real devices to speed up the execution of your test suite, and generates videos and logs to help you quickly identify issues with your app.
AWS Device Farm is designed for developers, QA teams, and customer support representatives who are building, testing, and supporting mobile apps to increase the quality of their apps. Application quality is increasingly important, and also getting complex due to the number of device models, variations in firmware and OS versions, carrier and manufacturer customizations, and dependencies on remote services and other apps. AWS Device Farm accelerates the development process by executing tests on multiple devices, giving developers, QA and support professionals the ability to perform automated tests and manual tasks like reproducing customer issues, exploratory testing of new functionality, and executing manual test plans. AWS Device Farm also offers significant savings by eliminating the need for internal device labs, lab managers, and automation infrastructure development.
How it works:
AWS Shield Advanced
provides expanded DDoS attack protection for web applications running on the following resources: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud, Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Route 53, AWS Global Accelerator.
aws lambda and fargate is serverless.
S3 Transfer Acceleration
Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration (S3TA) enables fast, easy, and secure transfers of files over long distances between your client and your Amazon S3 bucket. S3 Transfer Acceleration leverages Amazon CloudFront’s globally distributed AWS Edge Locations. As data arrives at an AWS Edge Location, data is routed to your Amazon S3 bucket over an optimized network path. S3 Transfer Acceleration is designed to optimize transfer speeds from across the world into S3 buckets. If you are uploading to a centralized bucket from geographically dispersed locations, or if you regularly transfer GBs or TBs of data across continents, you may save hours or days of data transfer time with S3 Transfer Acceleration.
Benefits of S3 Transfer Acceleration (S3TA): 
via - https://aws.amazon.com/s3/transfer-acceleration/

AWS Systems Manager gives you visibility and control of your infrastructure on AWS. Systems Manager provides a unified user interface so you can view operational data from multiple AWS services and allows you to automate operational tasks such as collecting software inventory, running commands, managing patches, and configuring servers across AWS Cloud as well as on-premises infrastructure.
AWS Systems Manager offers utilities for running commands, patch-management and configuration compliance:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/faq/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/faq/
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/
Warm Standby strategy
When selecting your DR strategy, you must weigh the benefits of lower RTO (recovery time objective) and RPO (recovery point objective) vs the costs of implementing and operating a strategy. The pilot light and warm standby strategies both offer a good balance of benefits and cost.
This strategy replicates data from the primary Region to data resources in the recovery Region, such as Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) DB instances or Amazon DynamoDB tables. These data resources are ready to serve requests. In addition to replication, this strategy requires you to create a continuous backup in the recovery Region. This is because when “human action” type disasters occur, data can be deleted or corrupted, and replication will replicate the bad data. Backups are necessary to enable you to get back to the last known good state.
The warm standby strategy deploys a functional stack, but at reduced capacity. The DR endpoint can handle requests, but cannot handle production levels of traffic. It may be more, but is always less than the full production deployment for cost savings. If the passive stack is deployed to the recovery Region at full capacity, however, then this strategy is known as “hot standby.” Because warm standby deploys a functional stack to the recovery Region, this makes it easier to test Region readiness using synthetic transactions.
DR strategies:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/architecture/disaster-recovery-dr-architecture-on-aws-part-iii-pilot-light-and-warm-standby/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/architecture/disaster-recovery-dr-architecture-on-aws-part-iii-pilot-light-and-warm-standby/
Incorrect options:
Multi-site active-active strategy - This strategy uses AWS Regions as your active sites, creating a multi-Region active/active architecture. Generally, two Regions are used. Each Region hosts a highly available, multi-Availability Zone (AZ) workload stack. In each Region, data is replicated live between the data stores and also backed up. This protects against disasters that include data deletion or corruption since the data backup can be restored to the last known good state. Each regional stack serves production traffic effectively. But, this strategy is cost involving and should only be used for mission-critical applications.
Pilot Light strategy - Pilot Light, like Warm Standby strategy, replicates data from the primary Region to data resources in the recovery Region, such as Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) DB instances or Amazon DynamoDB tables. But, the DR Region in a pilot light strategy (unlike warm standby) cannot serve requests until additional steps are taken. A pilot light in a home furnace does not provide heat to the home. It provides a quick way to light the furnace burners that then provide heat.
Warm standby can handle traffic at reduced levels immediately. Pilot light requires you to first deploy infrastructure and then scale out resources before the workload can handle requests.
Backup & Restore strategy - Backup and Restore is associated with higher RTO (recovery time objective) and RPO (recovery point objective). This results in longer downtimes and greater loss of data between when the disaster event occurs and recovery. However, backup and restore can still be the right strategy for workloads because it is the easiest and least expensive strategy to implement.
Reference:
EC2 Instance Connect
Amazon EC2 Instance Connect provides a simple and secure way to connect to your instances using Secure Shell (SSH). With EC2 Instance Connect, you use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies and principals to control SSH access to your instances, removing the need to share and manage SSH keys. All connection requests using EC2 Instance Connect are logged to AWS CloudTrail so that you can audit connection requests.
You can use Instance Connect to connect to your Linux instances using a browser-based client, the Amazon EC2 Instance Connect CLI, or the SSH client of your choice. EC2 Instance Connect can be used to connect to an EC2 instance from a Mac OS, Windows or Linux based computer.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/peering/what-is-vpc-peering.html
S3 is a key value based object storage service
S3 stores data in a flat non-hierarchical structure
Credential Reports
You can generate and download a credential report that lists all users in your account and the status of their various credentials, including passwords, access keys, and MFA devices. You can use credential reports to assist in your auditing and compliance efforts. You can use the report to audit the effects of credential lifecycle requirements, such as password and access key rotation. You can provide the report to an external auditor, or grant permissions to an auditor so that he or she can download the report directly.
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) provides a simple, scalable, fully managed elastic NFS file system for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources.
To access EFS file systems from on-premises, you must have an AWS Direct Connect or AWS VPN connection between your on-premises datacenter and your Amazon VPC. You mount an EFS file system on your on-premises Linux server using the standard Linux mount command for mounting a file system
Amazon S3 Replication
Replication enables automatic, asynchronous copying of objects across Amazon S3 buckets. Buckets that are configured for object replication can be owned by the same AWS account or by different accounts. You can copy objects between different AWS Regions or within the same Region. You can use replication to make copies of your objects that retain all metadata, such as the original object creation time and version IDs. This capability is important if you need to ensure that your replica is identical to the source object.
Exam Alert:
Amazon S3 supports two types of replication: Cross Region Replication vs Same Region Replication. Please review the differences between SRR and CRR:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/replication.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/replication.html
Amazon SQS
Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) is a fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. SQS eliminates the complexity and overhead associated with managing and operating message-oriented middleware, and empowers developers to focus on differentiating work.
Using SQS, you can send, store, and receive messages between software components at any volume, without losing messages or requiring other services to be available.
Incorrect options:
Amazon SNS - Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) is a highly available, durable, secure, fully managed pub/sub messaging service that enables you to decouple microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
Please review this reference architecture for building a decoupled order processing system using SNS and SQS:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/building-loosely-coupled-scalable-c-applications-with-amazon-sqs-and-amazon-sns/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/building-loosely-coupled-scalable-c-applications-with-amazon-sqs-and-amazon-sns/
Create tags for each department
You can assign metadata to your AWS resources in the form of tags. Each tag is a label consisting of a user-defined key and value. Tags can help you manage, identify, organize, search for, and filter resources. You can create tags to categorize resources by purpose, owner, environment, or other criteria.
Typically, you use business tags such as cost center/business unit, customer, or project to associate AWS costs with traditional cost-allocation dimensions. But a cost allocation report can include any tag. This lets you associate costs with technical or security dimensions, such as specific applications, environments, or compliance programs.
Example of tagging for cost optimization:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws_tagging.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws_tagging.html
AWS CloudHSM
The AWS CloudHSM service helps you meet corporate, contractual, and regulatory compliance requirements for data security by using a dedicated Hardware Security Module (HSM) instances within the AWS cloud.
CloudHSM allows you to securely generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys used for data encryption in a way that keys are accessible only by you.
How AWS CloudHSM works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/cloudhsm/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/cloudhsm/
AWS OpsWorks
AWS OpsWorks is a configuration management service that provides managed instances of Chef and Puppet. Chef and Puppet are automation platforms that allow you to use code to automate the configurations of your servers. OpsWorks lets you use Chef and Puppet to automate how servers are configured, deployed, and managed across your Amazon EC2 instances or on-premises compute environments.
AWS Glue - AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service that makes it easy for customers to prepare and load their data for analytics. AWS Glue job is meant to be used for batch ETL data processing.
How AWS Glue works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/glue/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/glue/
Convertible Reserved Instances
Purchase Convertible Reserved Instances if you need additional flexibility, such as the ability to use different instance families, operating systems, or tenancies over the Reserved Instance term. Convertible Reserved Instances provide you with a significant discount (up to 54%) compared to On-Demand Instances and can be purchased for a 1-year or 3-year term.
Convertible Reserved Instances can be useful when workloads are likely to change. In this case, a Convertible Reserved Instance enables you to adapt as needs evolve while still obtaining discounts and capacity reservations.
EC2 Pricing Options Overview:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/
Standard Reserved Instances - Standard Reserved Instances provide you with a significant discount (up to 72%) compared to On-Demand Instance pricing, and can be purchased for a 1-year or 3-year term. Standard Reserved Instances do not offer as much flexibility as Convertible Reserved Instances (such as not being able to change the instance family type), and therefore are not best-suited for this use case.
Review the differences between Standard Reserved Instances and Convertible Reserved Instances: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/cost-optimization-reservation-models/standard-vs.-convertible-offering-classes.html
LOAD balancing with Route 53 use Elastic Load balancer Route 53 does not load balance itself of the shell.
S3 Access Logs
Server access logging provides detailed records for the requests that are made to a bucket. Server access logs are useful for many applications. For example, access log information can be useful in security and access audits.
It can also help you learn about your customer base and understand your Amazon S3 bill.
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/architecture/well-architected/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/architecture/well-architected/
AWS DataSync
AWS DataSync is a secure online data transfer service that simplifies, automates, and accelerates copying terabytes of data to and from AWS storage services. Easily migrate or replicate large data sets without having to build custom solutions or oversee repetitive tasks. DataSync can copy data between Network File System (NFS) shares, or Server Message Block (SMB) shares, self-managed object storage, AWS Snowcone, Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file systems, and Amazon FSx for Windows File Server file systems.
You can use AWS DataSync for ongoing transfers from on-premises systems into or out of AWS for processing. DataSync can help speed up your critical hybrid cloud storage workflows in industries that need to move active files into AWS quickly. This includes machine learning in life sciences, video production in media and entertainment, and big data analytics in financial services. DataSync provides timely delivery to ensure dependent processes are not delayed. You can specify exclude filters, include filters, or both, to determine which files, folders or objects get transferred each time your task runs.
AWS DataSync employs an AWS-designed transfer protocol—decoupled from the storage protocol—to accelerate data movement. The protocol performs optimizations on how, when, and what data is sent over the network. Network optimizations performed by DataSync include incremental transfers, in-line compression, and sparse file detection, as well as in-line data validation and encryption.
Data Transfer between on-premises and AWS using DataSync:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/datasync/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/datasync/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/iam/identity-center/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/iam/identity-center/
Amazon Cognito
Amazon Cognito lets you add user sign-up, sign-in, and access control to your web and mobile apps quickly and easily. With Amazon Cognito, you also have the option to authenticate users through social identity providers such as Facebook, Twitter, or Amazon, with SAML identity solutions, or by using your own identity system.
S3 Lifecycle management
To manage your objects so that they are stored cost-effectively throughout their lifecycle, configure their Amazon S3 Lifecycle. An S3 Lifecycle configuration is a set of rules that define actions that Amazon S3 applies to a group of objects. There are two types of actions: Transition actions (define when objects transition to another storage class) and expiration actions (define when objects expire. Amazon S3 deletes expired objects on your behalf).
AWS Quick Starts references
Quick Starts are built by AWS solutions architects and partners to help you deploy popular technologies on AWS, based on AWS best practices for security and high availability. These accelerators reduce hundreds of manual procedures into just a few steps, so you can build your production environment quickly and start using it immediately.
Each Quick Start includes AWS CloudFormation templates that automate the deployment and a guide that discusses the architecture and provides step-by-step deployment instructions.
IAM access advisor
Access advisor shows the service permissions granted to a user and when those services were last accessed. You can use this information to revise your policies. To summarize, you can identify unnecessary permissions so that you can revise your IAM policies accordingly.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/ARG/latest/userguide/resource-groups.html
AWS Resource Groups - In AWS, a resource is an entity that you can work with. Examples include an Amazon EC2 instance, an AWS CloudFormation stack, or an Amazon S3 bucket. If you work with multiple resources, you might find it useful to manage them as a group rather than move from one AWS service to another for each task. If you manage large numbers of related resources, such as EC2 instances that make up an application layer, you likely need to perform bulk actions on these resources at one time.
You can use Resource Groups to organize your AWS resources. Resource groups make it easier to manage and automate tasks on large numbers of resources at a time. Resource Groups feature permissions are at the account level. As long as users who are sharing your account have the correct IAM permissions, they can work with resource groups that you create.
AWS CloudTrail Insights - AWS CloudTrail Insights helps AWS users identify and respond to unusual activity associated with write API calls by continuously analyzing CloudTrail management events.
Insights events are logged when CloudTrail detects unusual write management API activity in your account. If you have CloudTrail Insights enabled, and CloudTrail detects unusual activity, Insights events are delivered to the destination S3 bucket for your trail. You can also see the type of insight and the incident time period when you view Insights events on the CloudTrail console. Unlike other types of events captured in a CloudTrail trail, Insights events are logged only when CloudTrail detects changes in your account’s API usage that differ significantly from the account’s typical usage patterns.
CloudTrail Insights can help you detect unusual API activity in your AWS account by raising Insights events. CloudTrail Insights measures your normal patterns of API call volume, also called the baseline, and generates Insights events when the volume is outside normal patterns.
CloudTrail Insights continuously monitors CloudTrail write management events, and uses mathematical models to determine the normal levels of API and service event activity for an account. CloudTrail Insights identifies behavior that is outside normal patterns, generates Insights events, and delivers those events to a /CloudTrail-Insight folder in the chosen destination S3 bucket for your trail. You can also access and view Insights events in the AWS Management Console for CloudTrail.
Identify and Respond to Unusual API Activity using CloudTrail Insights:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/announcing-cloudtrail-insights-identify-and-respond-to-unusual-api-activity/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/announcing-cloudtrail-insights-identify-and-respond-to-unusual-api-activity/
Amazon Lightsail - Amazon Lightsail is the easiest way to get started with AWS for developers, small businesses, students, and other users who need a solution to build and host their applications on the cloud. Lightsail provides developers with compute, storage, and networking capacity and capabilities to deploy and manage websites and web applications in the cloud. Lightsail includes everything you need to launch your project quickly – virtual machines, containers, databases, CDN, load balancers, DNS management, etc. – for a low, predictable monthly price.
You can get preconfigured virtual private server plans that include everything to easily deploy and manage your application. Lightsail is best suited to projects that require a few virtual private servers and users who prefer a simple management interface. Common use cases for Lightsail include running websites, web applications, blogs, e-commerce sites, simple software, and more.
Also referred to as a bundle, a Lightsail plan includes a virtual server with a fixed amount of memory (RAM) and compute (vCPUs), SSD-based storage (disks), and a free data transfer allowance. Lightsail plans also offer static IP addresses (5 per account) and DNS management (3 domain zones per account). Lightsail plans are charged on an hourly, on-demand basis, so you only pay for a plan when you’re using it.
Lightsail offers a number of preconfigured, one-click-to-launch operating systems, development stacks, and web applications, including Linux and Windows OS, WordPress, LAMP, CentOS, and more.
The Elastic Beanstalk health monitoring can determine that the environment’s Auto Scaling group is available and has a minimum of at least one instance - In addition to Elastic Load Balancing health checks, Elastic Beanstalk monitors resources in your environment and changes health status to red if they fail to deploy, are not configured correctly, or become unavailable. These checks confirm that: 1. The environment’s Auto Scaling group is available and has a minimum of at least one instance. 2. The environment’s security group is available and is configured to allow incoming traffic on port 80. 3. The environment CNAME exists and is pointing to the right load balancer. 4. In a worker environment, the Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue is being polled at least once every three minutes.
With basic health reporting, the Elastic Beanstalk service does not publish any metrics to Amazon CloudWatch - With basic health reporting, the Elastic Beanstalk service does not publish any metrics to Amazon CloudWatch. The CloudWatch metrics used to produce graphs on the Monitoring page of the environment console are published by the resources in your environment.
AWS Quick Starts - AWS Quick Starts are automated reference deployments for key workloads on the AWS Cloud. Each Quick Start launches, configures and runs the AWS compute, network, storage, and other services required to deploy a specific workload on AWS, using AWS best practices for security and availability.
Quick Starts are accelerators that condense hundreds of manual procedures into just a few steps. They are fast, low-cost, and customizable. They are fully functional and designed for production.
Quick Starts include: 1. A reference architecture for the deployment 2. AWS CloudFormation templates (JSON or YAML scripts) that automate and configure the deployment 3. A deployment guide, which explains the architecture and implementation in detail, and provides instructions for customizing the deployment.
Quick Starts also include integrations that extend the cloud-based contact center functionality provided by Amazon Connect with key services and solutions from APN Partners—for customer relationship management (CRM), workforce optimization (WFO), analytics, unified communications (UC), and other use cases.
AWS Outposts - AWS Outposts is a fully managed service that offers the same AWS infrastructure, AWS services, APIs, and tools to virtually any data center, co-location space, or on-premises facility for a truly consistent hybrid experience. AWS Outposts is ideal for workloads that require low latency access to on-premises systems, local data processing, data residency, and migration of applications with local system interdependencies.
AWS compute, storage, database, and other services run locally on Outposts, and you can access the full range of AWS services available in the Region to build, manage, and scale your on-premises applications using familiar AWS services and tools.
You can use Outposts to support your applications that have low latency or local data processing requirements. These applications may need to generate near real-time responses to end-user applications or need to communicate with other on-premises systems or control on-site equipment. These can include workloads running on factory floors for automated operations in manufacturing, real-time patient diagnosis or medical imaging, and content and media streaming. You can use Outposts to securely store and process customer data that needs to remain on-premises or in countries where there is no AWS region. You can run data-intensive workloads on Outposts and process data locally when transmitting data to the cloud is expensive and wasteful and for better control on data analysis, back-up and restore.
How Outposts Works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/outposts/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/outposts/
AWS Well-Architected Tool - The AWS Well-Architected Tool helps you review the state of your workloads and compares them to the latest AWS architectural best practices. The tool is based on the AWS Well-Architected Framework, developed to help cloud architects build secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient application infrastructure.
To use this free tool, available in the AWS Management Console, just define your workload and answer a set of questions regarding operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, and cost optimization. The AWS Well-Architected Tool then provides a plan on how to architect for the cloud using established best practices.
The AWS Well-Architected Tool gives you access to knowledge and best practices used by AWS architects, whenever you need it. You answer a series of questions about your workload, and the tool delivers an action plan with step-by-step guidance on how to build better workloads for the cloud.
How Well-Architected Tool works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/well-architected-tool/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/well-architected-tool/
Amazon Elastic Transcoder - Amazon Elastic Transcoder lets you convert media files that you have stored in Amazon S3 into media files in the formats required by consumer playback devices. For example, you can convert large, high-quality digital media files into formats that users can playback on mobile devices, tablets, web browsers, and connected televisions.
Amazon Elastic Transcoder manages all aspects of the media transcoding process for you transparently and automatically. There’s no need to administer software, scale hardware, tune performance, or otherwise manage transcoding infrastructure. You simply create a transcoding “job” specifying the location of your source media file and how you want it transcoded. Amazon Elastic Transcoder also provides transcoding presets for popular output formats, which means that you don’t need to guess about which settings work best on particular devices. All these features are available via service API, AWS SDKs and the AWS Management Console.
https://aws.amazon.com/appstream2/
https://aws.amazon.com/workspaces/
Management events - An event in CloudTrail is the record of an activity in an AWS account. This activity can be an action taken by a user, role, or service that is monitorable by CloudTrail. CloudTrail events provide a history of both API and non-API account activity made through the AWS Management Console, AWS SDKs, command line tools, and other AWS services.
**There are three types of events that can be logged in CloudTrail: management events, data events, and CloudTrail Insights events.
By default, CloudTrail logs all management events and does not include data events or Insights events. Additional charges apply for data and Insights events. All event types use the same CloudTrail JSON log format.**
Management events provide information about management operations that are performed on resources in your AWS account. These are also known as control plane operations. Examples include registering devices, configuring rules for routing data, setting up logging etc.
AWS Cost Explorer - AWS Cost Explorer lets you explore your AWS costs and usage at both a high level and at a detailed level of analysis, and empowering you to dive deeper using a number of filtering dimensions (e.g., AWS Service, Region, Member Account, etc.) AWS Cost Explorer also gives you access to a set of default reports to help you get started, while also allowing you to create custom reports from scratch.
You can explore your usage and costs using the main graph, the Cost Explorer cost, and usage reports, or the Cost Explorer RI report. You can view data for up to the last 12 months, forecast how much you’re likely to spend for the next 12 months, and get recommendations for what Reserved Instances to purchase. You can use Cost Explorer to identify areas that need further inquiry and see trends that you can use to understand your costs.
You can view your costs and usage using the Cost Explorer user interface free of charge. You can also access your data programmatically using the Cost Explorer API.
When you first sign up for Cost Explorer, AWS prepares the data about your costs for the current month and the last 12 months and then calculates the forecast for the next 12 months. The current month’s data is available for viewing in about 24 hours. The rest of your data takes a few days longer. Cost Explorer updates your cost data at least once every 24 hours. After you sign up, Cost Explorer can display up to 12 months of historical data (if you have that much), the current month, and the forecasted costs for the next 12 months.
 via - https://aws.amazon.com/waf/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/waf/
AWS CloudTrail logs, Amazon VPC Flow Logs and Amazon GuardDuty findings - Amazon Detective can analyze trillions of events from multiple data sources such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Flow Logs, AWS CloudTrail, and Amazon GuardDuty, and automatically creates a unified, interactive view of your resources, users, and the interactions between them over time.
Amazon Detective conforms to the AWS shared responsibility model, which includes regulations and guidelines for data protection. Once enabled, Amazon Detective will process data from AWS CloudTrail logs, VPC Flow Logs, and Amazon GuardDuty findings for any accounts where it has been turned on.
Amazon Detective requires that you have Amazon GuardDuty enabled on your accounts for at least 48 hours before you enable Detective on those accounts. However, you can use Detective to investigate more than just your GuardDuty findings. Amazon Detective provides detailed summaries, analysis, and visualizations of the behaviors and interactions amongst your AWS accounts, EC2 instances, AWS users, roles, and IP addresses. This information can be very useful in understanding security issues or operational account activity.
How Amazon Detective Works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/detective/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/detective/
Amazon S3 Glacier Vault Lock - S3 Glacier Vault Lock allows you to easily deploy and enforce compliance controls for individual S3 Glacier vaults with a vault lock policy. You can specify controls such as “write once read many” (WORM) in a vault lock policy and lock the policy from future edits. Once locked, the policy can no longer be changed.
A vault lock policy can be locked to prevent future changes, providing strong enforcement for your compliance controls. You can use the vault lock policy to deploy regulatory and compliance controls, which typically require tight controls on data access.
As an example of a Vault Lock policy, suppose that you are required to retain archives for one year before you can delete them. To implement this requirement, you can create a Vault Lock policy that denies users permission to delete an archive until the archive has existed for one year. You can test this policy before locking it down. After you lock the policy, the policy becomes immutable.
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database - Amazon QLDB is a fully managed ledger database that provides a transparent, immutable, and cryptographically verifiable transaction log owned by a central trusted authority. Amazon QLDB can be used to track each and every application data change and maintains a complete and verifiable history of changes over time.
Ledgers are typically used to record a history of economic and financial activity in an organization. Many organizations build applications with ledger-like functionality because they want to maintain an accurate history of their applications’ data, for example, tracking the history of credits and debits in banking transactions, verifying the data lineage of an insurance claim, or tracing the movement of an item in a supply chain network. Ledger applications are often implemented using custom audit tables or audit trails created in relational databases.
Amazon QLDB is a new class of database that eliminates the need to engage in the complex development effort of building your own ledger-like applications. With QLDB, your data’s change history is immutable – it cannot be altered or deleted – and using cryptography, you can easily verify that there have been no unintended modifications to your application’s data. QLDB uses an immutable transactional log, known as a journal, that tracks each application data change and maintains a complete and verifiable history of changes over time. QLDB is easy to use because it provides developers with a familiar SQL-like API, a flexible document data model, and full support for transactions. QLDB’s streaming capability provides a near real-time flow of your data stored within QLDB, allowing you to develop event-driven workflows, real-time analytics, and to replicate data to other AWS services to support advanced analytical processing. QLDB is also serverless, so it automatically scales to support the demands of your application. There are no servers to manage and no read or write limits to configure. With QLDB, you only pay for what you use.
How Amazon Quantum Ledger Database Works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/qldb/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/qldb/
API Gateway can call an AWS Lambda function to create the front door of a serverless application - Amazon API Gateway is an AWS service for creating, publishing, maintaining, monitoring, and securing REST, HTTP, and WebSocket APIs at any scale. API developers can create APIs that access AWS or other web services, as well as data stored in the AWS Cloud.
API Gateway acts as a “front door” for applications to access data, business logic, or functionality from your backend services, such as workloads running on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), code running on AWS Lambda, any web application, or real-time communication applications.
API Gateway can be configured to send data directly to Amazon Kinesis Data Stream - Amazon API Gateway can execute AWS Lambda functions in your account, start AWS Step Functions state machines, or call HTTP endpoints hosted on AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Amazon EC2, and also non-AWS hosted HTTP based operations that are accessible via the public Internet.API Gateway also allows you to specify a mapping template to generate static content to be returned, helping you mock your APIs before the backend is ready. You can also integrate API Gateway with other AWS services directly – for example, you could expose an API method in API Gateway that sends data directly to Amazon Kinesis.
How API Gateway Works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/
AWS Elastic Beanstalk - There is no additional charge for AWS Elastic Beanstalk. You pay for AWS resources (e.g. EC2 instances or S3 buckets) you create to store and run your application. You only pay for what you use, as you use it; there are no minimum fees and no upfront commitments.
AWS Auto Scaling - There is no additional charge for AWS Auto Scaling. You pay only for the AWS resources needed to run your applications and Amazon CloudWatch monitoring fees.
CloudEndure Disaster Recovery - CloudEndure Disaster Recovery, available from the AWS Marketplace, continuously replicates server-hosted applications and server-hosted databases from any source into AWS using block-level replication of the underlying server. CloudEndure Disaster Recovery enables you to use AWS Cloud as a disaster recovery Region for an on-premises workload and its environment. It can also be used for disaster recovery of AWS hosted workloads if they consist only of applications and databases hosted on EC2 (i.e. not RDS).
Features of CloudEndure Disaster Recovery:
-
Continuous replication: CloudEndure Disaster Recovery provides continuous, asynchronous, block-level replication of your source machines into a staging area. This allows you to achieve sub-second Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs), since up-to-date applications are always ready to be spun up on AWS if a disaster strikes.
-
Low-cost staging area: Data is continually kept in sync in a lightweight staging area in your target AWS Region. The staging area contains low-cost resources that are automatically provisioned and managed by CloudEndure Disaster Recovery. This eliminates the need for duplicate resources and significantly reduces your disaster recovery total cost of ownership (TCO).
-
Automated machine conversion and orchestration: In the event of a disaster or drill, CloudEndure Disaster Recovery triggers a highly automated machine conversion process and a scalable orchestration engine that quickly spins up thousands of machines in your target AWS Region in parallel. This enables Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) of minutes. Unlike application-level solutions, CloudEndure Disaster Recovery replicates entire machines, including OS, system state configuration, system disks, databases, applications, and files.
-
Point-in-time recovery: Granular point-in-time recovery allows you to recover applications and IT environments that have been corrupted as a result of accidental system changes, ransomware, or other malicious attacks. In such cases, you can launch applications from a previous consistent point in time rather than launching applications in their most up-to-date state. During the recovery, you can select either the latest state or an earlier state from a list of points in time.
-
Easy, non-disruptive drills: With CloudEndure Disaster Recovery, you can conduct disaster recovery drills without disrupting your source environment or risking data loss. During drills, CloudEndure Disaster Recovery spins up machines in your target AWS Region in complete isolation to avoid network conflicts and performance impact.
-
Wide application and infrastructure support: Because CloudEndure Disaster Recovery replicates data at the block level, you can use it for all applications and databases that run on supported versions of Windows and Linux OS.
CloudEndure Disaster Recovery:  via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/disaster-recovery-workloads-on-aws/disaster-recovery-options-in-the-cloud.html
via - https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/disaster-recovery-workloads-on-aws/disaster-recovery-options-in-the-cloud.html
AWS IoT Core - AWS IoT Core lets you connect IoT devices to the AWS cloud without the need to provision or manage servers. AWS IoT Core can support billions of devices and trillions of messages and can process and route those messages to AWS endpoints and to other devices reliably and securely. With AWS IoT Core, your applications can keep track of and communicate with all your devices, all the time, even when they aren’t connected.
AWS IoT Core also makes it easy to use AWS and Amazon services like AWS Lambda, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon S3, Amazon SageMaker, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, Amazon QuickSight, and Alexa Voice Service to build IoT applications that gather, process, analyze and act on data generated by connected devices, without having to manage any infrastructure.
AWS IoT Core lets you select the communication protocol most appropriate for your use case to connect and manage IoT devices. AWS IoT Core supports MQTT (Message Queuing and Telemetry Transport), HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol - Secure), MQTT over WSS (WebSockets Secure), and LoRaWAN (low-power long-range wide-area network).
AWS IoT Core provides automated configuration and authentication upon a device’s first connection to AWS IoT Core, as well as end-to-end encryption throughout all points of connection, so that data is never exchanged between devices and AWS IoT Core without proven identity. In addition, you can secure access to your devices and applications by applying policies with granular permissions.
AWS IoT Core capabilities:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/iot-core/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/iot-core/
AWS OpsHub - AWS OpsHub is a graphical user interface you can use to manage your AWS Snowball devices, enabling you to rapidly deploy edge computing workloads and simplify data migration to the cloud. With just a few clicks in AWS OpsHub, you have the full functionality of the Snowball devices at your fingertips; you can unlock and configure devices, drag-and-drop data to devices, launch applications, and monitor device metrics.
Previously, customers operated Snowball devices by either entering commands into a command-line interface or by using REST APIs. Now with AWS OpsHub, you have an easier way to deploy and manage even large fleets of Snowball devices, all while operating without an internet connection.
AWS OpsHub takes all the existing operations available in the Snowball API and presents them as a simple graphical user interface. This interface helps you quickly and easily migrate data to the AWS Cloud and deploy edge computing applications on Snow Family Devices.
AWS OpsHub provides a unified view of AWS services that are running on Snow Family Devices and automates operational tasks through AWS Systems Manager. With AWS OpsHub, users with different levels of technical expertise can easily manage a large number of Snow Family Devices. With just a few clicks, you can unlock devices, transfer files, manage Amazon EC2 instances, and monitor device metrics.
When your Snow device arrives at your site, you download, install, and launch the AWS OpsHub application on a client machine, such as a laptop. After installation, you can unlock the device and start managing it and using supported AWS services locally. AWS OpsHub provides a dashboard that summarizes key metrics such as storage capacity and active instances on your device. It also provides a selection of the AWS services that are supported on the Snow Family Devices. Within minutes, you can begin transferring files to the device.
AWS Wavelength - AWS Wavelength is an AWS Infrastructure offering optimized for mobile edge computing applications. Wavelength Zones are AWS infrastructure deployments that embed AWS compute and storage services within communications service providers’ (CSP) data centers at the edge of the 5G network, so application traffic from 5G devices can reach application servers running in Wavelength Zones without leaving the telecommunications network. This avoids the latency that would result from application traffic having to traverse multiple hops across the Internet to reach their destination, enabling customers to take full advantage of the latency and bandwidth benefits offered by modern 5G networks.
AWS enterprise customers that build applications to serve their own use-cases such as IoT, live media production, and industrial automation can use Wavelength to deliver low-latency solutions. Customers with edge data processing needs such as image and video recognition, inference, data aggregation, and responsive analytics can use Wavelength to perform low-latency operations and processing right where their data is generated, reducing the need to move large amounts of data to be processed in centralized locations.
How Wavelength works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/wavelength/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/wavelength/
Compute Savings Plans, EC2 Instance Savings Plans - Savings Plans is a flexible pricing model that provides savings of up to 72% on your AWS compute usage. This pricing model offers lower prices on Amazon EC2 instances usage, regardless of instance family, size, OS, tenancy or AWS Region, and also applies to AWS Fargate and AWS Lambda usage.
Savings Plans offer significant savings over On-Demand, just like EC2 Reserved Instances, in exchange for a commitment to use a specific amount of compute power (measured in $/hour) for a one or three-year period. You can sign up for Savings Plans for a 1- or 3-year term and easily manage your plans by taking advantage of recommendations, performance reporting and budget alerts in the AWS Cost Explorer.
AWS offers two types of Savings Plans:
-
Compute Savings Plans provide the most flexibility and help to reduce your costs by up to 66%. These plans automatically apply to EC2 instance usage regardless of instance family, size, AZ, region, OS or tenancy, and also apply to Fargate and Lambda usage. For example, with Compute Savings Plans, you can change from C4 to M5 instances, shift a workload from EU (Ireland) to EU (London), or move a workload from EC2 to Fargate or Lambda at any time and automatically continue to pay the Savings Plans price.
-
EC2 Instance Savings Plans provide the lowest prices, offering savings up to 72% in exchange for a commitment to the usage of individual instance families in a region (e.g. M5 usage in N. Virginia). This automatically reduces your cost on the selected instance family in that region regardless of AZ, size, OS or tenancy. EC2 Instance Savings Plans give you the flexibility to change your usage between instances within a family in that region. For example, you can move from c5.xlarge running Windows to c5.2xlarge running Linux and automatically benefit from the Savings Plans prices.
How Savings Plans Work:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/savingsplans/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/savingsplans/
CloudTrail Logs, S3 Glacier, AWS Storage Gateway - By default, all data stored by AWS Storage Gateway in S3 is encrypted server-side with Amazon S3-Managed Encryption Keys (SSE-S3). Also, you can optionally configure different gateway types to encrypt stored data with AWS Key Management Service (KMS) via the Storage Gateway API.
Data at rest stored in S3 Glacier is automatically server-side encrypted using 256-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256) with keys maintained by AWS. If you prefer to manage your own keys, you can also use client-side encryption before storing data in S3 Glacier.
By default, the log files delivered by CloudTrail to your bucket are encrypted by Amazon server-side encryption with Amazon S3-managed encryption keys (SSE-S3). To provide a security layer that is directly manageable, you can instead use server-side encryption with AWS KMS–managed keys (SSE-KMS) for your CloudTrail log files. To use SSE-KMS with CloudTrail, you create and manage a KMS key, also known as a customer master key (CMK).
Amazon Quicksight - Amazon QuickSight is a scalable, serverless, embeddable, machine learning-powered business intelligence (BI) service built for the cloud. QuickSight lets you easily create and publish interactive BI dashboards that include Machine Learning-powered insights. QuickSight dashboards can be accessed from any device, and seamlessly embedded into your applications, portals, and websites.
With QuickSight, you can quickly embed interactive dashboards into your applications, websites, and portals. QuickSight provides a rich set of APIs and SDKs that allow you to easily customize the look and feel of the dashboards to match applications. With QuickSight, you can manage your dashboard versions, grant dashboard authoring privileges, and share usage reports with your end-customers. If your application is used by customers that belong to different teams or organizations, QuickSight ensures that their data is always siloed and secure.
Amazon QuickSight has a serverless architecture that automatically scales to tens of thousands of users without the need to set up, configure, or manage your own servers. It also ensures that your users don’t have to deal with slow dashboards during peak-hours when multiple BI users are accessing the same dashboards or datasets. And with pay-per-session pricing, you only pay when your users access the dashboards or reports, which makes it cost-effective for deployments with lots of users. There are no upfront costs or annual commitments for using QuickSight.
How QuickSight Works:  via - https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/
Connecting QuickSight to your Data Lakes (e.g. Amazon S3):  via - https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/
via - https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/